In vivo evidence for platelet-induced physiological angiogenesis by a COX driven mechanism
- PMID: 25238071
- PMCID: PMC4169573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107503
In vivo evidence for platelet-induced physiological angiogenesis by a COX driven mechanism
Abstract
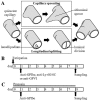
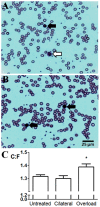
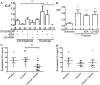
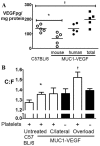
We sought to determine a role for platelets in in vivo angiogenesis, quantified by changes in the capillary to fibre ratio (C:F) of mouse skeletal muscle, utilising two distinct forms of capillary growth to identify differential effects. Capillary sprouting was induced by muscle overload, and longitudinal splitting by chronic hyperaemia. Platelet depletion was achieved by anti-GPIbα antibody treatment. Sprouting induced a significant increase in C:F (1.42±0.02 vs. contralateral 1.29±0.02, P<0.001) that was abolished by platelet depletion, while the significant C:F increase caused by splitting (1.40±0.03 vs. control 1.28±0.03, P<0.01) was unaffected. Granulocyte/monocyte depletion showed this response was not immune-regulated. VEGF overexpression failed to rescue angiogenesis following platelet depletion, suggesting the mechanism is not simply reliant on growth factor release. Sprouting occurred normally following antibody-induced GPVI shedding, suggesting platelet activation via collagen is not involved. BrdU pulse-labelling showed no change in the proliferative potential of cells associated with capillaries after platelet depletion. Inhibition of platelet activation by acetylsalicylic acid abolished sprouting, but not splitting angiogenesis, paralleling the response to platelet depletion. We conclude that platelets differentially regulate mechanisms of angiogenesis in vivo, likely via COX signalling. Since endothelial proliferation is not impaired, we propose a link between COX1 and induction of endothelial migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Egginton S, Zhou AL, Brown MD, Hudlická O (2001) Unorthodox angiogenesis in skeletal muscle. Cardiovasc Res 49: 34–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhou AL, Egginton S, Brown MD, Hudlická O (1998) Capillary growth in overloaded, hypertrophic adult rat skeletal muscle: an ultrastructural study. Anat Rec 252: 49–63. - PubMed
-
- Zhou AL, Egginton S, Hudlická O Brown MD (1998) Internal division of capillaries in rat skeletal muscle in response to, chronic vasodilator treatment with alpha1-antagonist prazosin. Cell Tissue Res 293: 293–303. - PubMed
-
- Wragg JW, Durant S, McGettrick HM, Sample KM, Egginton S, et al. (2014) Shear stress regulated gene expression and angiogenesis in vascular endothelium. Microcirculation 21: 290–300. - PubMed
-
- Pinedo HM, Verheul HM, D′Amato RJ, Folkman J (1998) Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet 352: 1775–1777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

