HBx inhibits CYP2E1 gene expression via downregulating HNF4α in human hepatoma cells
- PMID: 25238230
- PMCID: PMC4169590
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107913
HBx inhibits CYP2E1 gene expression via downregulating HNF4α in human hepatoma cells
Abstract
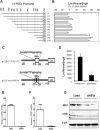
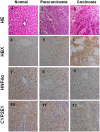
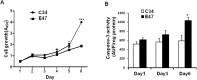
CYP2E1, one of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidases located predominantly in liver, plays a key role in metabolism of xenobiotics including ethanol and procarcinogens. Recently, down-expression of CYP2E1 was found in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with the majority to be chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers. In this study, we tested a hypothesis that HBx may inhibit CYP2E1 gene expression via hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α). By enforced HBx gene expression in cultured HepG2 cells, we determined the effect of HBx on CYP2E1 mRNA and protein expression. With a bioinformatics analysis, we found a consensus HNF-4α binding sequence located on -318 to -294 bp upstream of human CYP2E1 promoter. Using reporter gene assay and site-directed mutagenesis, we have shown that mutation of this site dramatically decreased CYP2E1 promoter activity. By silencing endogenous HNF-4α, we have further validated knockdown of HNF-4α significantly decreased CYP2E1 expression. Ectopic overexpression of HBx in HepG2 cells inhibits HNF-4α expression, and HNF-4α levels were inversely correlated with viral proteins both in HBV-infected HepG2215 cells and as well as HBV positive HCC liver tissues. Moreover, the HBx-induced CYP2E1 reduction could be rescued by ectopic supplement of HNF4α protein expression. Furthermore, human hepatoma cells C34, which do not express CYP2E1, shows enhanced cell growth rate compared to E47, which constitutively expresses CYP2E1. In addition, the significantly altered liver proteins in CYP2E1 knockout mice were detected with proteomics analysis. Together, HBx inhibits human CYP2E1 gene expression via downregulating HNF4α which contributes to promotion of human hepatoma cell growth. The elucidation of a HBx-HNF4α-CYP2E1 pathway provides novel insight into the molecular mechanism underlining chronic HBV infection associated hepatocarcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Schutte K, Bornschein J, Malfertheiner P (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiological trends and risk factors. Dig Dis 27: 80–92. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132: 2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Kew MC (2010) Epidemiology of chronic hepatitis B virus infection, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Biol (Paris) 58: 273–277. - PubMed
-
- Brechot C, Kremsdorf D, Soussan P, Pineau P, Dejean A, et al. (2010) Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): molecular mechanisms and novel paradigms. Pathol Biol (Paris) 58: 278–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

