Structure-based design of potent and selective Leishmania N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors
- PMID: 25238611
- PMCID: PMC4211304
- DOI: 10.1021/jm5011397
Structure-based design of potent and selective Leishmania N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors
Abstract
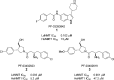
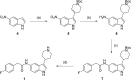
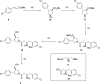
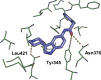
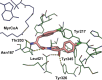
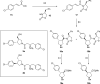
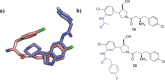
Inhibitors of Leishmania N-myristoyltransferase (NMT), a potential target for the treatment of leishmaniasis, obtained from a high-throughput screen, were resynthesized to validate activity. Crystal structures bound to Leishmania major NMT were obtained, and the active diastereoisomer of one of the inhibitors was identified. On the basis of structural insights, enzyme inhibition was increased 40-fold through hybridization of two distinct binding modes, resulting in novel, highly potent Leishmania donovani NMT inhibitors with good selectivity over the human enzyme.
Figures
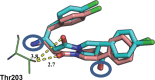
References
-
- Leishmaniasis: Burden and Distribution; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2013; http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/burden/en (accessed July 1, 2014).
-
- den Boer M.; Argaw D.; Jannin J.; Alvar J. Leishmaniasis impact and treatment access. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Sundar S. Drug resistance in Indian visceral leishmaniasis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2001, 6, 849–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

