Protein-energy wasting and uremic failure to thrive in children with chronic kidney disease: they are not small adults
- PMID: 25239300
- PMCID: PMC4282521
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-014-2898-0
Protein-energy wasting and uremic failure to thrive in children with chronic kidney disease: they are not small adults
Abstract
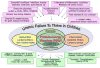
Protein-energy wasting (PEW), a condition of decreased body protein and fat mass, is highly prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and a potent predictor of mortality in this population. In adults with CKD, PEW has typically been defined on the basis of (1) deranged biochemical parameters, (2) reduced body mass, (3) reduced muscle mass, and (4) decreased dietary protein intake. Emerging data suggest that PEW may also commonly afflict children with CKD and have a negative impact on growth and development ("uremic failure to thrive"), yet it remains comparatively understudied and less well characterized in these patients. Given the challenges of applying adult-defined PEW criteria to the pediatric population, the authors of a recent study entitled "Protein energy wasting in children with chronic kidney disease" [Abraham et al. (2014) Pediatr Nephrol 29:1231-1238] have sought to develop a scoring system and three alterative definitions for this condition using a combination of biochemical markers, clinical measurements, and subjective reporting in children in the CKiD cohort: (1) minimal PEW definition (≥2 adult-defined PEW criteria); (2) standard PEW definition (≥3 adult-defined PEW criteria); (3) modified PEW definition (≥3 adult-defined PEW criteria, plus short stature or poor growth). These authors observed that meeting the modified PEW definition was associated with a significantly increased risk of hospitalization in unadjusted analyses, i.e., a 2.2-fold higher risk, and trended towards increased risk in multivariable adjusted analyses, i.e., 2.0-fold higher risk. At the present time, future studies validating these findings and developing further refined definitions and/or scoring systems for the detection and management of PEW in children and uremic failure to thrive are urgently needed.
Conflict of interest statement
No relevant conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
Figures
Comment on
-
Protein energy wasting in children with chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2014 Jul;29(7):1231-8. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-2768-9. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24504731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim JC, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD. Frailty and protein-energy wasting in elderly patients with end stage kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:337–351. - PubMed
-
- Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, Cano N, Chauveau P, Cuppari L, Franch H, Guarnieri G, Ikizler TA, Kaysen G, Lindholm B, Massy Z, Mitch W, Pineda E, Stenvinkel P, Trevino-Becerra A, Wanner C. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73:391–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical