Incidence of erythropoietin antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia: the Prospective Immunogenicity Surveillance Registry (PRIMS)
- PMID: 25239637
- PMCID: PMC4339685
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfu297
Incidence of erythropoietin antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia: the Prospective Immunogenicity Surveillance Registry (PRIMS)
Abstract
Background: Subcutaneous administration of Eprex(®) (epoetin alfa) in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) was contraindicated in the European Union between 2002 and 2006 after increased reports of anti-erythropoietin antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia (PRCA). The Prospective Immunogenicity Surveillance Registry (PRIMS) was conducted to estimate the incidence of antibody-mediated PRCA with subcutaneous administration of a new coated-stopper syringe presentation of Eprex(®) and to compare this with the PRCA incidence with subcutaneous NeoRecormon(®) (epoetin beta) and Aranesp(®) (darbepoetin alfa).
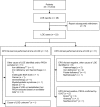
Methods: PRIMS was a multicentre, multinational, non-interventional, parallel-group, immunogenicity surveillance registry. Adults with CKD receiving or about to initiate subcutaneous Eprex(®), NeoRecormon(®) or Aranesp(®) for anaemia were enrolled and followed for up to 3 years. Unexplained loss or lack of effect (LOE), including suspected PRCA, was reported, with antibody testing for confirmation of PRCA.
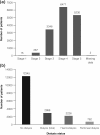
Results: Of the 15 333 patients enrolled, 5948 received Eprex(®) (8377 patient-years) and 9356 received NeoRecormon(®)/Aranesp(®) (14 286 patient-years). No treatment data were available for 29 patients. Among 23 patients with LOE, five cases of PRCA were confirmed (Eprex(®), n = 3; NeoRecormon(®), n = 1; Aranesp(®), n = 1). Based on exposed time, PRCA incidence was 35.8/100 000 patient-years (95% CI 7.4-104.7) for Eprex(®) versus 14.0/100 000 patient-years (95% CI 1.7-50.6) for NeoRecormon(®)/Aranesp(®). The incidence of PRCA with Eprex(®) was not significantly different versus comparator ESAs (rate ratio: 2.56; 95% CI 0.43-15.31). An analysis based on observed time produced similar findings.
Conclusion: This large, prospective registry demonstrates that PRCA is rare with subcutaneous administration of either the new coated-stopper syringe presentation of Eprex(®), or NeoRecormon(®) or Aranesp(®).
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; darbepoetin alfa; epoetin alfa; epoetin beta; pure red cell aplasia.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pure red cell aplasia with anti-erythropoietin antibodies occurs more commonly with one formulation of epoetin alfa than another.Curr Med Res Opin. 2004 Jan;20(1):83-6. doi: 10.1185/030079903125002702. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004. PMID: 14741076 Review.
-
Anti-erythropoietin antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia after treatment with recombinant erythropoietin products: recommendations for minimization of risk.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Oct;15(10):2728-34. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000140219.28618.9F. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 15466278
-
Pure red cell aplasia and anti-erythropoietin antibodies in patients treated with epoetin.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003 Nov;18 Suppl 8:viii37-41. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1091. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. PMID: 14608000 Review.
-
Pure red-cell aplasia and epoetin therapy.N Engl J Med. 2004 Sep 30;351(14):1403-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040528. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 15459301
-
Epoetin-associated pure red cell aplasia: past, present, and future considerations.Transfusion. 2008 Aug;48(8):1754-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2008.01749.x. Epub 2008 May 14. Transfusion. 2008. PMID: 18482185 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complexing Protein-Free Botulinum Neurotoxin A Formulations: Implications of Excipients for Immunogenicity.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Feb 10;16(2):101. doi: 10.3390/toxins16020101. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38393178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anaemia and beyond.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Mar;12(3):157-68. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.193. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26656456 Review.
-
Discovery of JTZ-951: A HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Renal Anemia.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017 Nov 20;8(12):1320-1325. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00404. eCollection 2017 Dec 14. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 29259755 Free PMC article.
-
Harms of off-label erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for critically ill people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 25;8(8):CD010969. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010969.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28841235 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational Modifications and the Immunogenicity of Biotherapeutics.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:5358272. doi: 10.1155/2016/5358272. Epub 2016 Apr 14. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27191002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pollock C, Johnson DW, Hörl WH, et al. Pure red cell aplasia induced by erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Rossert J, Casadevall N, Eckardt KU. Anti-erythropoietin antibodies and pure red cell aplasia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:398–406. - PubMed
-
- Boven K, Knight J, Bader F, et al. Epoetin-associated pure red cell aplasia in patients with chronic kidney disease: solving the mystery. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20(Suppl 3):iii33–iii40. - PubMed
-
- Casadevall N. Pure red cell aplasia and anti-erythropoietin antibodies in patients treated with epoetin. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18(Suppl 8):viii37–viii41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

