Cardiac P2X purinergic receptors as a new pathway for increasing Na⁺ entry in cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 25239801
- PMCID: PMC4233301
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00553.2014
Cardiac P2X purinergic receptors as a new pathway for increasing Na⁺ entry in cardiac myocytes
Abstract
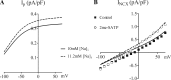
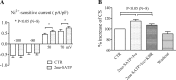
P2X4 receptors (P2X4Rs) are ligand-gated ion channels capable of conducting cations such as Na(+). Endogenous cardiac P2X4R can mediate ATP-activated current in adult murine cardiomyocytes. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that cardiac P2X receptors can induce Na(+) entry and modulate Na(+) handling. We further determined whether P2X receptor-induced stimulation of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) has a role in modulating the cardiac contractile state. Changes in Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase current (Ip) and NCX current (INCX) after agonist stimulation were measured in ventricular myocytes of P2X4 transgenic mice using whole cell patch-clamp techniques. The agonist 2-methylthio-ATP (2-meSATP) increased peak Ip from a basal level of 0.52 ± 0.02 to 0.58 ± 0.03 pA/pF. 2-meSATP also increased the Ca(2+) entry mode of INCX (0.55 ± 0.09 pA/pF under control conditions vs. 0.82 ± 0.14 pA/pF with 2-meSATP) at a membrane potential of +50 mV. 2-meSATP shifted the reversal potential of INCX from -14 ± 2.3 to -25 ± 4.1 mV, causing an estimated intracellular Na(+) concentration increase of 1.28 ± 0.42 mM. These experimental results were closely mimicked by mathematical simulations based on previously established models. KB-R7943 or a structurally different agent preferentially opposing the Ca(2+) entry mode of NCX, YM-244769, could inhibit the 2-meSATP-induced increase in cell shortening in transgenic myocytes. Thus, the Ca(2+) entry mode of INCX participates in P2X agonist-stimulated contractions. In ventricular myocytes from wild-type mice, the P2X agonist could increase INCX, and KB-R7943 was able to inhibit the contractile effect of endogenous P2X4Rs, indicating a physiological role of these receptors in wild-type cells. The data demonstrate a novel Na(+) entry pathway through ligand-gated P2X4Rs in cardiomyocytes.
Keywords: Na+-K+-ATPase; Na+/Ca2+ exchanger; contraction; myocytes; purinergic receptors.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Banfi C, Ferrario S, De Vincenti O, Ceruti S, Fumagalli M, Mazzola A, D'Ambrosi N, Volonte C, Fratto P, Vitali E, Burnstock G, Beltrami E, Parolari A, Polvani G, Biglioli P, Tremoli E, Abbracchio MP. P2 receptors in human heart: upregulation of P2X6 in patients undergoing heart transplantation, interaction with TNFα and potential role in myocardial cell death. J Mol Cell Cardiol 39: 929–939, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bers D. Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force (Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine). Dordrecht: Springer, 2008.
-
- Carmeliet E. A fuzzy subsarcolemmal space for intracellular Na+ in cardiac cells? Cardiovasc Res 26: 433–442, 1992. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Guzman M, Soto F, Gomez-Hernandez JM, Lund PE, Stuhmer W. Characterization of recombinant human P2X4 receptor reveals pharmacological differences to the rat homologue. Mol Pharmacol 51: 109–118, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg KS, Bers DM. Isoproterenol does not enhance Ca-dependent Na/Ca exchange current in intact rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 39: 972–981, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

