Transcription factor networks in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 25242320
- PMCID: PMC4403667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.038
Transcription factor networks in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
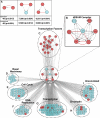
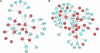
Specific cellular fates and functions depend on differential gene expression, which occurs primarily at the transcriptional level and is controlled by complex regulatory networks of transcription factors (TFs). TFs act through combinatorial interactions with other TFs, cofactors, and chromatin-remodeling proteins. Here, we define protein-protein interactions using a coaffinity purification/mass spectrometry method and study 459 Drosophila melanogaster transcription-related factors, representing approximately half of the established catalog of TFs. We probe this network in vivo, demonstrating functional interactions for many interacting proteins, and test the predictive value of our data set. Building on these analyses, we combine regulatory network inference models with physical interactions to define an integrated network that connects combinatorial TF protein interactions to the transcriptional regulatory network of the cell. We use this integrated network as a tool to connect the functional network of genetic modifiers related to mastermind, a transcriptional cofactor of the Notch pathway.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adryan B, Teichmann SA. FlyTF: a systematic review of site-specific transcription factors in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1532–3. - PubMed
-
- Araujo SJ, Cela C, Llimargas M. Tramtrack regulates different morphogenetic events during Drosophila tracheal development. Development. 2007;134:3665–3676. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signalling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Babu MM, Luscombe NM, Aravind L, Gerstein M, Teichmann SA. Structure and evolution of transcriptional regulatory networks. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:283–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

