Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line
- PMID: 25242904
- PMCID: PMC4167841
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-459
Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line
Abstract
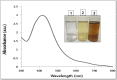
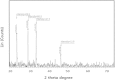
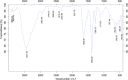
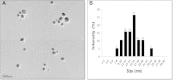
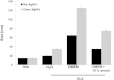
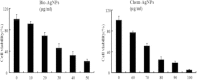
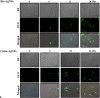
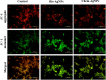
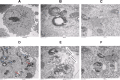
The goal of the present study was to investigate the toxicity of biologically prepared small size of silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cells A549. Herein, we describe a facile method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles by treating the supernatant from a culture of Escherichia coli with silver nitrate. The formation of silver nanoparticles was characterized using various analytical techniques. The results from UV-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis show a characteristic strong resonance centered at 420 nm and a single crystalline nature, respectively. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirmed the possible bio-molecules responsible for the reduction of silver from silver nitrate into nanoparticles. The particle size analyzer and transmission electron microscopy results suggest that silver nanoparticles are spherical in shape with an average diameter of 15 nm. The results derived from in vitro studies showed a concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability when A549 cells were exposed to silver nanoparticles. This decrease in cell viability corresponded to increased leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), increased intracellular reactive oxygen species generation (ROS), and decreased mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MTP). Furthermore, uptake and intracellular localization of silver nanoparticles were observed and were accompanied by accumulation of autophagosomes and autolysosomes in A549 cells. The results indicate that silver nanoparticles play a significant role in apoptosis. Interestingly, biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles showed more potent cytotoxicity at the concentrations tested compared to that shown by chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles. Therefore, our results demonstrated that human lung epithelial A549 cells could provide a valuable model to assess the cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma cells A549; Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); Mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MTP); Reactive oxygen species generation (ROS); Silver nanoparticles (AgNP).
Figures
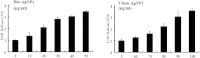
Similar articles
-
Multidimensional effects of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter felis, and human lung (L132) and lung carcinoma A549 cells.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2015 Feb 5;10:35. doi: 10.1186/s11671-015-0747-0. eCollection 2015. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2015. PMID: 25852332 Free PMC article.
-
Facile coconut inflorescence sap mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its diverse antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jun;111:110834. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110834. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32279817
-
Comparative assessment of the apoptotic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus tequilensis and Calocybe indica in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: targeting p53 for anticancer therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Jun 29;10:4203-22. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S83953. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26170659 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis induction in lung and prostate cancer cells through silver nanoparticles synthesized from Pinus roxburghii bioactive fraction.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020 Feb;25(1):23-37. doi: 10.1007/s00775-019-01729-3. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 31641851
-
Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Lasiosiphon eriocephalus (Decne): In vitro Assessment of their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023;11(2):180-193. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666221207153116. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36503464
Cited by
-
Palladium Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Apoptosis, and Immunomodulation Enhance the Biogenesis and Release of Exosome in Human Leukemia Monocytic Cells (THP-1).Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Apr 15;16:2849-2877. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S305269. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33883895 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of silver nanoparticles in Ehrlich carcinoma-bearing mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;391(12):1421-1430. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1558-5. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30178417
-
Antimicrobial efficacy of platinum-doped silver nanoparticles.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020 Nov;108(8):3393-3401. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34674. Epub 2020 Jul 3. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32618123 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of salinomycin and silver nanoparticles enhances apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells: an effective anticancer therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Aug 2;11:3655-75. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S111279. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27536105 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 13;17(9):1534. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091534. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27649147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen X, Schluesener HJ. Nanosilver: a nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol Lett. 2008;176(1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Park EJ, Yi J, Kim Y, Choi K, Park K. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol In Vitro. 2010;24(3):872–878. - PubMed
-
- Arora S, Rajwade JM, Paknikar KM. Nanotoxicology and in vitro studies: the need of the hour. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;258(2):151–165. - PubMed
-
- Gurunathan S, Kalishwaralal K, Vaidyanathan R, Venkataraman D, Pandian SR, Muniyandi J, Hariharan N, Eom SH. Biosynthesis, purification and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2009;74(1):328–335. - PubMed
-
- Li XQ, Xu HZ, Chen ZS, Chen GF. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms and their applications. J Nanomater. 2011;2011:270974.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

