Impact of age and gender on the prevalence and prognostic importance of the metabolic syndrome and its components in Europeans. The MORGAM Prospective Cohort Project
- PMID: 25244618
- PMCID: PMC4171109
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107294
Impact of age and gender on the prevalence and prognostic importance of the metabolic syndrome and its components in Europeans. The MORGAM Prospective Cohort Project
Erratum in
-
Correction: Impact of Age and Gender on the Prevalence and Prognostic Importance of the Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in Europeans. The MORGAM Prospective Cohort Project.PLoS One. 2015 May 15;10(5):e0128848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128848. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25978324 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the influence of age and gender on the prevalence and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in Europeans presenting with the Metabolic Syndrome (MetS).
Methods: Using 36 cohorts from the MORGAM-Project with baseline between 1982-1997, 69094 men and women aged 19-78 years, without known CVD, were included. During 12.2 years of follow-up, 3.7%/2.1% of men/women died due to CVD. The corresponding percentages for fatal and nonfatal coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke were 8.3/3.8 and 3.1/2.5.
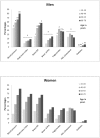
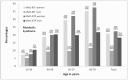
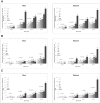
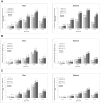
Results: The prevalence of MetS, according to modified definitions of the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the revised National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP-ATPIII), increased across age groups for both genders (P<0.0001); with a 5-fold increase in women from ages 19-39 years to 60-78 years (7.4%/7.6% to 35.4%/37.6% for IDF/NCEP-ATPIII) and a 2-fold increase in men (5.3%/10.5% to 11.5%/21.8%). Using multivariate-adjusted Cox regressions, the associations between MetS and all three CVD events were significant (P<0.0001). For IDF/NCEP-ATPIII in men and women, hazard ratio (HR) for CHD was 1.60/1.62 and 1.93/2.03, for CVD mortality 1.73/1.65 and 1.77/2.06, and for stroke 1.51/1.53 and 1.58/1.77. Whereas in men the HRs for CVD events were independent of age (MetS*age, P>0.05), in women the HRs for CHD declined with age (HRs 3.23/3.98 to 1.55/1.56; MetS*age, P=0.01/P=0.001 for IDF/NCEP-ATPIII) while the HRs for stroke tended to increase (HRs 1.31/1.25 to 1.55/1.83; MetS*age, P>0.05).
Conclusion: In Europeans, both age and gender influenced the prevalence of MetS and its prognostic significance. The present results emphasise the importance of being critical of MetS in its current form as a marker of CVD especially in women, and advocate for a redefinition of MetS taking into account age especially in women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Reaven GM (1988) Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37: 1595–1607. - PubMed
-
- Qiao Q (2006) The DECODE Study Group (2006) Comparison of different definitions of the metabolic syndrome in relation to cardiovascular mortality in European men and women. Diabetologia 49: 2837–2846. - PubMed
-
- Ascaso JF, Millán J, Mateo-Gallego R, Ruiz A, Suarez-Tembra M, et al. (2011) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in a hypertriglyceridemic population. Eur J Intern Med 22: 177–1781. - PubMed
-
- Benetos A, Thomas F, Pannier B, Bean K, Jégo B, et al. (2008) All-cause and cardiovascular mortality using the different definitions of metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol 102: 188–191. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Guerra R, Fox G, Cullen P, Schulte H, et al. (2007) Harmonizing the definition of the metabolic syndrome: comparison of the criteria of the Adult Treatment Panel III and the International Diabetes Federation in United States of American and European populations. Am J Cardiol 99: 541–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

