Evaluation of acoustic membrane microparticle (AMMP) technology for a sensitive ligand binding assay to support pharmacokinetic determinations of a biotherapeutic
- PMID: 25245223
- PMCID: PMC4389748
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-014-9659-7
Evaluation of acoustic membrane microparticle (AMMP) technology for a sensitive ligand binding assay to support pharmacokinetic determinations of a biotherapeutic
Abstract
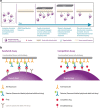
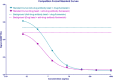
Achieving the required sensitivity can be a challenge in the development of ligand binding assays for pharmacokinetic (PK) determinations of biotherapeutics. To address this need, BioScale's Acoustic Membrane Microparticle (AMMP) technology was evaluated for the quantification of a PEGylated domain antibody (dAb) biotherapeutic. Previous uses of this technology had shown utility in biomarker and process development applications and this is the first application, to our knowledge, for PK determinations. In this evaluation, AMMP was capable of delivering a sensitivity of 0.750 ng/mL, which surpasses the sensitivity requirements for the majority of assays to support PK determinations. This evaluation demonstrates that this emerging technology has the ability to produce the required sensitivity, reproducibility, and selectivity needed to meet the industry's standards for PK analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of a Generic Anti-PEG Antibody Assay Using BioScale's Acoustic Membrane MicroParticle Technology.AAPS J. 2015 Nov;17(6):1511-6. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9799-4. Epub 2015 Jul 3. AAPS J. 2015. PMID: 26139446 Free PMC article.
-
Developing custom chinese hamster ovary-host cell protein assays using acoustic membrane microparticle technology.J Vis Exp. 2011 Feb 3;(48):2493. doi: 10.3791/2493. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21339717 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing matrix effects in ligand-binding assays through the use of new reagents and technology.Bioanalysis. 2014 Apr;6(8):1059-67. doi: 10.4155/bio.14.75. Bioanalysis. 2014. PMID: 24830890
-
Bioanalysis of target biomarker and PK/PD relevancy during the development of biotherapeutics.Bioanalysis. 2012 Oct;4(20):2513-23. doi: 10.4155/bio.12.220. Bioanalysis. 2012. PMID: 23157359 Review.
-
Surface plasmon resonance biosensing.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;503:65-88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-567-5_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19151937 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Technologies and Generic Assays for the Detection of Anti-Drug Antibodies.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:6262383. doi: 10.1155/2016/6262383. Epub 2016 Jul 31. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27556048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generic Anti-PEG Antibody Assay on ProterixBio's (Formerly BioScale) ViBE Platform Shows Poor Reproducibility.AAPS J. 2018 Apr 24;20(3):65. doi: 10.1208/s12248-018-0228-3. AAPS J. 2018. PMID: 29691672
-
Development of a Generic Anti-PEG Antibody Assay Using BioScale's Acoustic Membrane MicroParticle Technology.AAPS J. 2015 Nov;17(6):1511-6. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9799-4. Epub 2015 Jul 3. AAPS J. 2015. PMID: 26139446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zambito F KA, Zhang Y, DeSilva B. Development of a PK immunoassay for a therapeutic monoclonal antibody using optimiser technology. Poster presented at: National Biotechnology Conference. 2013 May 22–23; San Diego CA.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

