FNR regulates expression of important virulence factors contributing to pathogenicity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 25245807
- PMCID: PMC4249304
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02315-14
FNR regulates expression of important virulence factors contributing to pathogenicity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
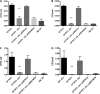
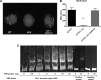
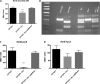
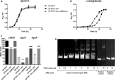
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) is responsible for the majority of urinary tract infections (UTIs), which are some of the world's most common bacterial infections of humans. Here, we examined the role of FNR (fumarate and nitrate reduction), a well-known global regulator, in the pathogenesis of UPEC infections. We constructed an fnr deletion mutant of UPEC CFT073 and compared it to the wild type for changes in virulence, adherence, invasion, and expression of key virulence factors. Compared to the wild type, the fnr mutant was highly attenuated in the mouse model of human UTI and showed severe defects in adherence to and invasion of bladder and kidney epithelial cells. Our results showed that FNR regulates motility and multiple virulence factors, including expression of type I and P fimbriae, modulation of hemolysin expression, and expression of a novel pathogenicity island involved in α-ketoglutarate metabolism under anaerobic conditions. Our results demonstrate that FNR is a key global regulator of UPEC virulence and controls expression of important virulence factors that contribute to UPEC pathogenicity.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterization of a Phase-Variable Element That Regulates the Autotransporter UpaE in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.mBio. 2018 Aug 7;9(4):e01360-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01360-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30087170 Free PMC article.
-
Iron limitation induces motility in uropathogenic E. coli CFT073 partially through action of LpdA.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0104824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01048-24. Epub 2024 Jun 14. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38874412 Free PMC article.
-
PafR, a novel transcription regulator, is important for pathogenesis in uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2014 Oct;82(10):4241-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00086-14. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25069986 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors of uropathogenic E. coli and their interaction with the host.Adv Microb Physiol. 2014;65:337-72. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Adv Microb Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25476769 Review.
-
Pathogenomics of uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012 Apr-Jun;30(2):141-9. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.96657. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22664427 Review.
Cited by
-
ArcA Controls Metabolism, Chemotaxis, and Motility Contributing to the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2015 Sep;83(9):3545-54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00312-15. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26099584 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Control of Dual Transporters Involved in α-Ketoglutarate Utilization Reveals Their Distinct Roles in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2017 Feb 21;8:275. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00275. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28270808 Free PMC article.
-
Global transcriptional regulator FNR regulates the pyruvate cycle and proton motive force to play a role in aminoglycosides resistance of Edwardsiella tarda.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 7;13:1003586. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1003586. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160231 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible Metabolism and Suppression of Latent Enzymes Are Important for Escherichia coli Adaptation to Diverse Environments within the Host.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jul 24;201(16):e00181-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00181-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31160397 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and Fitness of Urinary Tract Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Jun;3(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0016-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0016-2015. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26185076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guest JR, Green J, Irvine AS, Spiro S. 1996. The FNR modulon and FNR-regulated gene expression, p 317–342 In Lin ECC, Lynch AS. (ed), Regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. R. G. Landes & Co, Austin, TX.
-
- Kiley PJ, Beinert H. 1999. Oxygen sensing by the global regulator, FNR: the role of the iron-sulfur cluster. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 22:341–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

