Interactive neonatal gastrointestinal magnetic resonance imaging using fruit juice as an oral contrast media
- PMID: 25245815
- PMCID: PMC4186814
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2342-14-33
Interactive neonatal gastrointestinal magnetic resonance imaging using fruit juice as an oral contrast media
Abstract
Background: The objective was to evaluate the use of fruit juice with an interactive inversion recovery (IR) MR pulse sequence to visualise the gastrointestinal tract.
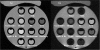
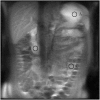
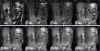
Methods: We investigated the relaxation properties of 12 different natural fruit juices in vitro, to identify which could be used as oral contrast. We then describe our initial experience using an interactive MR pulse sequence to allow optimal visualisation after administering pineapple juice orally, and suppressing pre-existing bowel fluid contents, with variable TI in three adult and one child volunteer.
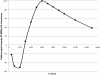
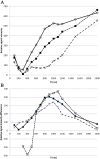
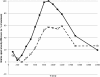
Results: Pineapple juice (PJ) had both the shortest T1 (243 ms) and shortest T2 (48 ms) of the fruit juices tested. Optimal signal differentiation between pre-existing bowel contents and oral PJ administration was obtained with TIs of between 900 and 1100 ms.
Conclusion: The use of an inversion recovery preparation allowed long T1 pre-existing bowel contents to be suppressed whilst the short T1 of fruit juice acts as a positive contrast medium. Pineapple juice could be used as oral contrast agent for neonatal gastrointestinal magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Sizemore AW, Rabbani KZ, Ladd A, Applegate KE. Diagnostic performance of the upper gastrointestinal series in the evaluation of children with clinically suspected malrotation. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:518–528. - PubMed
-
- Daneman A. Malrotation: the balance of evidence. Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39:S164–S166. - PubMed
-
- Graves MJ, Wong P, Black RT, Lomas DJ. MR fluoroscopy employing interactive pulse sequence switching. Proc ISMRM. 2007;15:1654.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

