Mastl is required for timely activation of APC/C in meiosis I and Cdk1 reactivation in meiosis II
- PMID: 25246615
- PMCID: PMC4178961
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201406033
Mastl is required for timely activation of APC/C in meiosis I and Cdk1 reactivation in meiosis II
Abstract
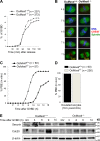
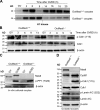
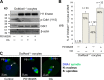
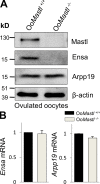
In mitosis, the Greatwall kinase (called microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase like [Mastl] in mammals) is essential for prometaphase entry or progression by suppressing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activity. PP2A suppression in turn leads to high levels of Cdk1 substrate phosphorylation. We have used a mouse model with an oocyte-specific deletion of Mastl to show that Mastl-null oocytes resume meiosis I and reach metaphase I normally but that the onset and completion of anaphase I are delayed. Moreover, after the completion of meiosis I, Mastl-null oocytes failed to enter meiosis II (MII) because they reassembled a nuclear structure containing decondensed chromatin. Our results show that Mastl is required for the timely activation of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome to allow meiosis I exit and for the rapid rise of Cdk1 activity that is needed for the entry into MII in mouse oocytes.
© 2014 Adhikari et al.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mastl/PP2A regulate Cdk1 in ooycte maturation.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 7;6(22):18734-5. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4916. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26299916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Álvarez-Fernández, M., Sánchez-Martínez R., Sanz-Castillo B., Gan P.P., Sanz-Flores M., Trakala M., Ruiz-Torres M., Lorca T., Castro A., and Malumbres M.. 2013. Greatwall is essential to prevent mitotic collapse after nuclear envelope breakdown in mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110:17374–17379 10.1073/pnas.1310745110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, H.Y., Jennings P.C., Stewart J., Verrills N.M., and Jones K.T.. 2011. Essential role of protein phosphatase 2A in metaphase II arrest and activation of mouse eggs shown by okadaic acid, dominant negative protein phosphatase 2A, and FTY720. J. Biol. Chem. 286:14705–14712 10.1074/jbc.M110.193227 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

