Population specific impact of genetic variants in KCNJ11 gene to type 2 diabetes: a case-control and meta-analysis study
- PMID: 25247988
- PMCID: PMC4172481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107021
Population specific impact of genetic variants in KCNJ11 gene to type 2 diabetes: a case-control and meta-analysis study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Potassium inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11 (KCNJ11) gene have a key role in insulin secretion and is of substantial interest as a candidate gene for type 2 diabetes (T2D). The current work was performed to delineate the genetic influence of KCNJ11 polymorphisms on risk of T2D in South Indian population through case-control association study along with systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods: A case-control study of 400 T2D cases and controls of South Indian origin were performed to analyze the association of KCNJ11 polymorphisms (rs5219, rs5215, rs41282930, rs1800467) and copy number variations (CNV) on the risk of T2D. In addition a systematic review and meta-analysis for KCNJ11 rs5219 was conducted in 3,831 cases and 3,543 controls from 5 published reports from South-Asian population by searching various databases. Odds ratio with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to assess the association strength. Cochran's Q, I2 statistics were used to study heterogeneity between the eligible studies.
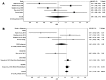
Results: KCNJ11 rs5215, C-G-C-C haplotype and two loci analysis (rs5219 vs rs1800467) showed a significant association with T2D but CNV analysis did not show significant variation between T2D cases and control subjects. Lower age of disease onset (P = 0.04) and higher body mass index (BMI) (P = 0.04) were associated with rs5219 TT genotype in T2D patients. The meta-analysis of KCNJ11 rs5219 on South Asian population showed no association on susceptibility to T2D with an overall pooled OR = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.83-1.16. Stratification analysis showed East Asian population and global population were associated with T2D when compared to South Asians.
Conclusion: KCNJ11 rs5219 is not independently associated with T2D in South-Indian population and our meta-analysis suggests that KCNJ11 polymorphism (rs5219) is associated with risk of T2D in East Asian population and global population but this outcome could not be replicated in South Asian sub groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Association between polymorphisms of microsomal epoxide hydrolase and COPD: results from meta-analyses.Respirology. 2008 Nov;13(6):837-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2008.01356.x. Respirology. 2008. PMID: 18811882
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Precision Medicine in Lifestyle Medicine: The Way of the Future?Am J Lifestyle Med. 2019 Mar 20;14(2):169-186. doi: 10.1177/1559827619834527. eCollection 2020 Mar-Apr. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2019. PMID: 32231483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular complications in KCNJ11, HHEX and SLC30A8 genetic polymorphisms carriers: A case-control study.Heliyon. 2021 Nov 17;7(11):e08376. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08376. eCollection 2021 Nov. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34849419 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Diabetes-Associated Genetic Polymorphisms as Potential Disease Predictors.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Dec 18;12:2689-2706. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S230061. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31908510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diversity of 'Very Important Pharmacogenes' in two South-Asian populations.PeerJ. 2021 Nov 10;9:e12294. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12294. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34824904 Free PMC article.
-
Admixture Has Shaped Romani Genetic Diversity in Clinically Relevant Variants.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 16;12:683880. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.683880. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34220960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, et al. (2004) Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med 350: 1838–1849. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L, Clement JPt, Gonzalez G, Kunjilwar K, Babenko A, et al. (1998) Toward understanding the assembly and structure of KATP channels. Physiol Rev 78: 227–245. - PubMed
-
- Hansen SK, Nielsen EM, Ek J, Andersen G, Glumer C, et al. (2005) Analysis of separate and combined effects of common variation in KCNJ11 and PPARG on risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90: 3629–3637. - PubMed
-
- Hani EH, Boutin P, Durand E, Inoue H, Permutt MA, et al. (1998) Missense mutations in the pancreatic islet beta cell inwardly rectifying K+ channel gene (KIR6.2/BIR): a meta-analysis suggests a role in the polygenic basis of Type II diabetes mellitus in Caucasians. Diabetologia 41: 1511–1515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

