Standard basic emergency obstetric and neonatal care training in Addis Ababa; trainees reaction and knowledge acquisition
- PMID: 25248410
- PMCID: PMC4181417
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-14-201
Standard basic emergency obstetric and neonatal care training in Addis Ababa; trainees reaction and knowledge acquisition
Abstract
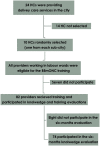
Background: In 2010, the Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia (FMOH) has developed standard Basic Emergency Obstetric and Neonatal Care (BEmONC) in-service training curricula to respond to the high demand for competency in EmONC. However, the effectiveness of the training curricula has not been well documented. A collaborative intervention project in Addis Ababa has trained providers using the standard BEmONC curricula where this paper presents Krikpartick level 1 and level 2 evaluation of the training.
Methods: The project has been conducted in 10 randomly selected public health centers (HC) in Addis Ababa. Providers working in the labour wards of the selected HCs have received the standard BEmONC training between May and July 2013. Using standard tools, trainees' reaction to the course and factual knowledge during the immediate post-course and six months after the training were assessed. Descriptive statistics and t-tests were done.
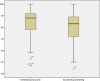
Results: Of the total 82 providers who received the training, 30 (36.6%) were male, 61 (74.4%) were midwives. Providers' work experiences ranged from 1 month to 37 years. Seventy-four (89%) providers reported that the training was appropriate for their work, 95% reported that the training have updated their knowledge & skills, while 27 (32.9%) reported that the training facilities & arrangements were unsatisfactory. The mean immediate post-course knowledge score was 83.5% and 33 (40%) providers did not achieve knowledge-based mastery in their first attempt. The midwives were more likely to achieve knowledge-based mastery than the nurses (p < 0.05). The mean knowledge score six-months post-training was 80.2% and 40% have scored knowledge based mastery.
Conclusions: Being one of the first papers reporting the implementation of the standard in-service BEmONC training curriculum, we have identified an important limitation on the course evaluations of the curriculum, which need urgent consideration. The majority of the trainees has reported favourable reaction to the training, but many of them did not achieve knowledge-based mastery in the immediate post training although the knowledge retention six months post training was encouraging.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF . Levels in Trends in Child Mortality; Estimates Developed by the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. Geneva, Switzerland: UNICEF; 2013.
-
- Bhutta ZA, Chopra M, Axelson H, Berman P, Boerma T, Bryce J, Bustreo F, Cavagnero E, Cometto G, Daelmans B, de Francisco A, Fogstad H, Gupta N, Laski L, Lawn J, Maliqi B, Mason E, Pitt C, Requejo J, Starrs A, Victora CG, Wardlaw T. Countdown to 2015 decade report (2000-10): taking stock of maternal, newborn, and child survival. Lancet. 2010;375(9730):2032–2044. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60678-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO/UNICEF . Countdown to 2015 decade report (2000–2010): taking stock of maternal, newborn and child survival. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6920/14/201/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources