Red cell distribution width is an independent factor for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 25248504
- PMCID: PMC4543415
- DOI: 10.1007/s10157-014-1033-7
Red cell distribution width is an independent factor for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: The increased value of the red cell distribution width (RDW) was reported to indicate poor prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure. We evaluated the value of the RDW in the diagnosis of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) in patients without diastolic heart failure among the chronic kidney disease (CKD) population.
Methods: The study group consisted of 73 ambulatory patients with CKD, stages 2-5. Standard echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) were performed, and the level of RDW was determined. Patients were divided into four groups according to the results of peak early diastolic velocity of mitral annulus (EmLV) and the stage of CKD: group with early stage CKD (eGFR > 30 ml/min/1.73 m(2)) without LVDD (EmLV ≥ 8 cm/s), early stage CKD with LVDD (EmLV < 8 cm/s), group with advanced stage CKD (eGFR ≤ 30 ml/min/1.73 m(2)) without LVDD, and group with advanced stage CKD with LVDD.
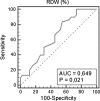
Results: Patients with advanced stage CKD with LVDD were characterized by higher RDW levels than patients with advanced stage CKD without LVDD and with early stage CKD groups with and without LVDD [14.5 (13.8-19.5) % vs. 13.7 (11.4-15,4) %, p = 0.049, vs. 13.8(13.1-14.9) %, p = 0.031, vs. 13.7(12.1-16.2) %, p = 0.0007], respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of RDW level for the detection of LVDD was 0.649, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.528-0.758, p = 0.021, whereas ROC derived RDW value of >13.5 % was characterized by a sensitivity of 83.3 % and specificity of 45.2 % for predicting LVDD. The only independent factor of LVDD was RDW level >13.5 % with odds ratio (OR) = 3.92 (95 % CI 1.05-14.56), p = 0.037.
Conclusion: RDW can be used as an additional factor for the diagnosis of LVDD in patients with advanced stage of CKD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyperuricemia is an independent predictive factor for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jan-Feb;24(1):47-54. doi: 10.17219/acem/38159. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25923086
-
Hypocalcemia is related to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease.J Cardiol. 2014 Mar;63(3):198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24012332
-
Left-ventricular diastolic dysfunction in Korean children with chronic kidney disease: data from the KNOW-Ped CKD study.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Dec 9;21(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02152-6. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33297989 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Impact of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease.Contrib Nephrol. 2018;195:81-91. doi: 10.1159/000486938. Epub 2018 May 7. Contrib Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29734153 Review.
-
[Diastolic Dysfunction in CKD: Cause or Effect?s].G Ital Nefrol. 2025 Feb 28;42(1):2025-vol1. doi: 10.69097/42-01-2025-04. G Ital Nefrol. 2025. PMID: 40026223 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Is Associated With Adverse Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;9:877220. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.877220. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35755057 Free PMC article.
-
Value of red blood cell distribution width in prediction of diastolic dysfunction in cirrhotic cardiomyopathy.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 21;29(15):2322-2335. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2322. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37124890 Free PMC article.
-
The Predictive Role of Red Cell Distribution Width in Mortality among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0162025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162025. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27906969 Free PMC article.
-
High red cell distribution width at the time of ST segment elevation myocardial infarction is better at predicting diastolic than systolic left ventricular dysfunction: A single-center prospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 May;97(18):e0601. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010601. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29718862 Free PMC article.
-
Association between red cell distribution width and mortality in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 3;7:45632. doi: 10.1038/srep45632. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28367961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das Gupta A, Hegde C, Mistri R. Red cell distribution width as a measure of severity of iron deficiency in iron deficiency anaemia. Indian J Med Res. 1994;1994(100):177–183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

