Genome-wide association study in Chinese identifies novel loci for blood pressure and hypertension
- PMID: 25249183
- PMCID: PMC4303798
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu478
Genome-wide association study in Chinese identifies novel loci for blood pressure and hypertension
Abstract
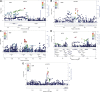
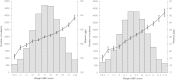
Hypertension is a common disorder and the leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease and premature deaths worldwide. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) in the European population have identified multiple chromosomal regions associated with blood pressure, and the identified loci altogether explain only a small fraction of the variance for blood pressure. The differences in environmental exposures and genetic background between Chinese and European populations might suggest potential different pathways of blood pressure regulation. To identify novel genetic variants affecting blood pressure variation, we conducted a meta-analysis of GWASs of blood pressure and hypertension in 11 816 subjects followed by replication studies including 69 146 additional individuals. We identified genome-wide significant (P < 5.0 × 10(-8)) associations with blood pressure, which included variants at three new loci (CACNA1D, CYP21A2, and MED13L) and a newly discovered variant near SLC4A7. We also replicated 14 previously reported loci, 8 (CASZ1, MOV10, FGF5, CYP17A1, SOX6, ATP2B1, ALDH2, and JAG1) at genome-wide significance, and 6 (FIGN, ULK4, GUCY1A3, HFE, TBX3-TBX5, and TBX3) at a suggestive level of P = 1.81 × 10(-3) to 5.16 × 10(-8). These findings provide new mechanistic insights into the regulation of blood pressure and potential targets for treatments.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis reveals transethnic replication of mean arterial and pulse pressure loci.Hypertension. 2013 Nov;62(5):853-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01148. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 24001895 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variations in CYP17A1, CACNB2 and PLEKHA7 are associated with blood pressure and/or hypertension in She ethnic minority of China.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Dec;219(2):709-14. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.09.006. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21963141
-
Blood pressure and hypertension are associated with 7 loci in the Japanese population.Circulation. 2010 Jun 1;121(21):2302-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.904664. Epub 2010 May 17. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 20479155
-
ATP2B1 gene polymorphisms rs2681472 and rs17249754 are associated with susceptibility to hypertension and blood pressure levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 16;100(15):e25530. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025530. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33847678 Free PMC article.
-
Recapitulation of four hypertension susceptibility genes (CSK, CYP17A1, MTHFR, and FGF5) in East Asians.Metabolism. 2013 Feb;62(2):196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.07.008. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 22959498 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variants in LRP1 and ULK4 Are Associated with Acute Aortic Dissections.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Sep 1;99(3):762-769. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.06.034. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27569546 Free PMC article.
-
A prediction model for the impact of environmental and genetic factors on cardiovascular events: development in a salt substitutes population.J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 30;21(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03899-w. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36717874 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variation in Steroid and Xenobiotic Metabolizing Pathways and Enterolactone Excretion Before and After Flaxseed Intervention in African American and European American Women.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019 Feb;28(2):265-274. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0826. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019. PMID: 30709839 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Associations of the hypertension-related single nucleotide polymorphism rs11191548 with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and leptin in Chinese children.BMC Med Genet. 2018 Jan 16;19(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0523-y. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29338791 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the A46G polymorphism (rs1042713) in the β2-adrenergic receptor gene and essential hypertension susceptibility in the Chinese population: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e23164. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023164. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kearney P.M., Whelton M., Reynolds K., Muntner P., Whelton P.K., He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Kupper N., Willemsen G., Riese H., Posthuma D., Boomsma D.I., de Geus E.J. Heritability of daytime ambulatory blood pressure in an extended twin design. Hypertension. 2005;45:80–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

