The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 25249263
- PMCID: PMC4286720
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x
The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
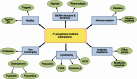
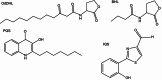
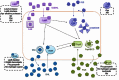
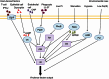
Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes severe and persistent infections in immune compromised individuals and cystic fibrosis sufferers. The infection is hard to eradicate as P. aeruginosa has developed strong resistance to most conventional antibiotics. The problem is further compounded by the ability of the pathogen to form biofilm matrix, which provides bacterial cells a protected environment withstanding various stresses including antibiotics. Quorum sensing (QS), a cell density-based intercellular communication system, which plays a key role in regulation of the bacterial virulence and biofilm formation, could be a promising target for developing new strategies against P. aeruginosa infection. The QS network of P. aeruginosa is organized in a multi-layered hierarchy consisting of at least four interconnected signaling mechanisms. Evidence is accumulating that the QS regulatory network not only responds to bacterial population changes but also could react to environmental stress cues. This plasticity should be taken into consideration during exploration and development of anti-QS therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Abe A, Matsuzawa T, Kuwae A. Type-III effectors: sophisticated bacterial virulence factors. C R Biol. 2005;328:413–428. - PubMed
-
- Adam EC, Mitchell BS, Schumacher DU, Grant G, Schumacher U. Pseudomonas aeruginosa II lectin stops human ciliary beating: therapeutic implications of fucose. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;155:2102–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

