Hepatitis E in Germany--an under-reported infectious disease
- PMID: 25249359
- PMCID: PMC4174681
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2014.0577
Hepatitis E in Germany--an under-reported infectious disease
Abstract
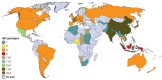
Background: At least 17% of the population in Germany has been infected with the hepatitis E virus (HEV); thus, HEV infections are more frequent than was previously assumed. However, fewer than 500 HEV infections were reported to the Robert Koch Institute in 2013.
Method: Review of pertinent literature retrieved by a selective search in PubMed.
Results: Persons living in Germany generally acquire hepatitis E infection within the country by consuming infected and undercooked pork; in rare cases, hepatitis E infections are imported from the tropics. HEV can be transmitted via blood products, blood transfusions, and organ transplantation. More than 99% of HEV infections are asymptomatic and self-limiting, but there are also severe cases with acute liver failure. Immunosuppressed persons can develop chronic HEV infection, potentially leading, within a few years, to liver cirrhosis with life-threatening sequelae. Moreover, HEV infection may be associated with extrahepatic manifestations such as Guillain-Barré syndrome. In two retrospectively evaluated case series, ribavirin was found to be active against HEV and can be used to treat either acute or chronic HEV infection.
Conclusion: Hepatitis E must be considered in the differential diagnosis of elevated hepatic enzyme levels and of systemic and neurological conditions of uncertain origin. The infection is usually self-limiting but can take a severe course in immunosuppressed persons. In such cases, ribavirin can be used as an antiviral treatment.
Figures


Comment in
-
Current data.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015 Mar 27;112(13):220. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2015.0220a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015. PMID: 25869340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In reply.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015 Mar 27;112(13):220. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2015.0220b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2015. PMID: 25869341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wedemeyer H, Pischke S, Manns MP. Pathogenesis and treatment of hepatitis E virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1388–1397. - PubMed
-
- Rein DB, Stevens GA, Theaker J, Wittenborn JS, Wiersma ST. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatology. 2011;55:988–997. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shukri> I, Davidson E, Tan A, et al. Rash and arthralgia caused by hepatitis E. Lancet. 2013;382 - PubMed
-
- van den Berg B, Annemick A, Van der Eijk A, et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with preceding hepatitis E virus infection. Neurology. 2014 epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

