Cup position alone does not predict risk of dislocation after hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 25249516
- PMCID: PMC4270833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2014.07.009
Cup position alone does not predict risk of dislocation after hip arthroplasty
Abstract
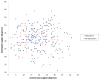
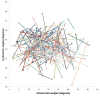
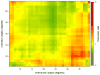
We used a large prospective institutional registry to determine if there is a 'safe zone' that exists for acetabular component position within which the risk of hip dislocation is low and if other patient and implant factors affect the risk of hip dislocation. Patients who reported a dislocation event within six months after hip arthroplasty surgery were identified, and acetabular component position was measured with anteroposterior radiographs. The frequency of dislocation was 2.1% (147 of 7040 patients). No significant difference was found in the number of dislocated hips among the radiographic zones (±5°,±10°,±15° boundaries). Dislocators <50 years old were less active preoperatively than nondislocators (P=0.006). Acetabular component position alone is not protective against instability.
Keywords: arthroplasty; cup orientation; dislocation; hip; safe zone.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What Safe Zone? The Vast Majority of Dislocated THAs Are Within the Lewinnek Safe Zone for Acetabular Component Position.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Feb;474(2):386-91. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4432-5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26150264 Free PMC article.
-
The Safe Zone Range for Cup Anteversion Is Narrower Than for Inclination in THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Feb;476(2):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000051. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529664 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between operative and radiographic acetabular component orientation: which factors influence resultant cup orientation?Bone Joint J. 2014 Oct;96-B(10):1290-7. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.96B10.34100. Bone Joint J. 2014. PMID: 25274911
-
Reducing the risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: the effect of orientation of the acetabular component.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005 Jun;87(6):762-9. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.87B6.14745. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. PMID: 15911655 Review.
-
Modern cup alignment techniques in total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Sep;105(5):907-913. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.03.015. Epub 2019 May 1. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31054840
Cited by
-
The Impingement-free, Prosthesis-specific, and Anatomy-adjusted Combined Target Zone for Component Positioning in THA Depends on Design and Implantation Parameters of both Components.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Aug;478(8):1904-1918. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001233. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 32732575 Free PMC article.
-
Acetabular cup version modelling and its clinical applying on plain radiograms.World J Orthop. 2017 Dec 18;8(12):929-934. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.929. eCollection 2017 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2017. PMID: 29312852 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Acetabular Version after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Comparison of Two Radiographic Methods.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021 Aug;56(4):513-516. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721360. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 34483397 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of spinopelvic relationship among Turkish orthopedic surgeons in total joint replacement: a survey.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2024 Nov 8;58(5):296-300. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2024.23085. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2024. PMID: 39560971 Free PMC article.
-
Lewinnek zone not "the be-all and end-all" functional planning for acetabular component positioning in total hip arthroplasty.Arthroplasty. 2025 Jan 6;7(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s42836-024-00284-w. Arthroplasty. 2025. PMID: 39757219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Vail TP, Berry DJ. The Epidemiology of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Jt Surg. 2009;91:128–33. - PubMed
-
- Amstutz HC, Kody MH. Hip Arthroplasty. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1991. Dislocation and subluxation; pp. 429–48.
-
- Beaulé PE, Schmalzried TP, Udomkiat P, Amstutz HC. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A:256–63. - PubMed
-
- Eftekhar NS. Dislocation and instability complicating low friction arthroplasty of the hip joint. Clin Orthop. 1976:120–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

