Leptospira mayottensis sp. nov., a pathogenic species of the genus Leptospira isolated from humans
- PMID: 25249563
- PMCID: PMC4811635
- DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.066597-0
Leptospira mayottensis sp. nov., a pathogenic species of the genus Leptospira isolated from humans
Abstract
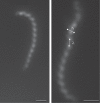
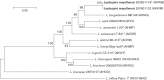
A group of strains representing species of the genus Leptospira, isolated from patients with leptospirosis in Mayotte (Indian Ocean), were previously found to be considerably divergent from other known species of the genus Leptospira. This was inferred from sequence analysis of rrs (16S rRNA) and other genetic loci and suggests that they belong to a novel species. Two strains from each serogroup currently identified within this novel species were studied. Spirochaete, aerobic, motile, helix-shaped strains grew well at 30-37 °C, but not at 13 °C or in the presence of 8-azaguanine. Draft genomes of the strains were also analysed to study the DNA relatedness with other species of the genus Leptospira. The new isolates formed a distinct clade, which was most closely related to Leptospira borgpetersenii, in multilocus sequence analysis using concatenated sequences of the genes rpoB, recA, fusA, gyrB, leuS and sucA. Analysis of average nucleotide identity and genome-to-genome distances, which have recently been proposed as reliable substitutes for classical DNA-DNA hybridization, further confirmed that these isolates should be classified as representatives of a novel species. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 39.5 mol%. These isolates are considered to represent a novel species, for which the name Leptospira mayottensis sp. nov. is proposed, with 200901116(T) ( = CIP 110703(T) = DSM 28999(T)) as the type strain.
© 2014 IUMS.
Figures

References
-
- Bourhy P., Collet L., Lernout T., Zinini F., Hartskeerl R. A., van der Linden H., Thiberge J. M., Diancourt L., Brisse S. & other authors (2012). Human leptospira isolates circulating in Mayotte (Indian Ocean) have unique serological and molecular features. J Clin Microbiol 50, 307–311. 10.1128/JCM.05931-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brenner D. J., Kaufmann A. F., Sulzer K. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Rogers F. C., Weyant R. S. (1999). Further determination of DNA relatedness between serogroups and serovars in the family Leptospiraceae with a proposal for Leptospira alexanderi sp. nov. and four new Leptospira genomospecies. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49, 839–858. 10.1099/00207713-49-2-839 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bulach D. M., Zuerner R. L., Wilson P., Seemann T., McGrath A., Cullen P. A., Davis J., Johnson M., Kuczek E. & other authors (2006). Genome reduction in Leptospira borgpetersenii reflects limited transmission potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103, 14560–14565. 10.1073/pnas.0603979103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

