Elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist, versus subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for the treatment of endometriosis: effects on bone mineral density
- PMID: 25249568
- PMCID: PMC4212335
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719114549848
Elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist, versus subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for the treatment of endometriosis: effects on bone mineral density
Abstract
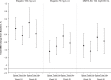
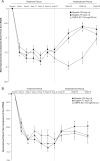
This randomized double-blind study, with 24-week treatment and 24-week posttreatment periods, evaluated the effects of elagolix (150 mg every day, 75 mg twice a day) versus subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA-SC) on bone mineral density (BMD), in women with endometriosis-associated pain (n = 252). All treatments induced minimal mean changes from baseline in BMD at week 24 (elagolix 150 mg: -0.11%/-0.47%, elagolix 75 mg: -1.29%/-1.2%, and DMPA-SC: 0.99%/-1.29% in the spine and total hip, respectively), with similar or less changes at week 48 (posttreatment). Elagolix was associated with improvements in endometriosis-associated pain, assessed with composite pelvic signs and symptoms score (CPSSS) and visual analogue scale, including statistical noninferiority to DMPA-SC in dysmenorrhea and nonmenstrual pelvic pain components of the CPSSS. The most common adverse events (AEs) in elagolix groups were headache, nausea, and nasopharyngitis, whereas the most common AEs in the DMPA-SC group were headache, nausea, upper respiratory tract infection, and mood swings. This study showed that similar to DMPA-SC, elagolix treatment had minimal impact on BMD over a 24-week period and demonstrated similar efficacy on endometriosis-associated pain.
Keywords: GnRH antagonists; elagolix; endometriosis; pelvic pain.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment of Endometriosis-Associated Pain with Elagolix, an Oral GnRH Antagonist.N Engl J Med. 2017 Jul 6;377(1):28-40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1700089. Epub 2017 May 19. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28525302 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy, tolerability, and bone density outcomes of elagolix with add-back therapy for endometriosis-associated pain: twelve months of an ongoing randomized phase 3 trial.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024 Dec;231(6):630.e1-630.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2024.06.040. Epub 2024 Jun 30. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38955323 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Elagolix in Women With Endometriosis: Results From Two Extension Studies.Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;132(1):147-160. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002675. Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29889764 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of elagolix in the treatment of endometriosis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;18(13):1391-1397. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2017.1359258. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28737050 Review.
-
Elagolix (Orilissa)--an oral GnRH antagonist for endometriosis pain.Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2018 Sep 24;60(1556):158-160. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2018. PMID: 30383729 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Medical Treatment for Endometriosis: Tolerability, Quality of Life and Adherence.Front Glob Womens Health. 2021 Sep 27;2:729601. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2021.729601. eCollection 2021. Front Glob Womens Health. 2021. PMID: 34816243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of quality of life in patients with endometriosis undergoing treatment with progestins, oral contraceptives pills (OCP), and GnRH agonists.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03937-3. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40836300 Free PMC article.
-
Elagolix: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2018 Sep;78(14):1501-1508. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0977-4. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30194661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review to determine use of the Endometriosis Health Profiles to measure quality of life outcomes in women with endometriosis.Hum Reprod Update. 2024 Mar 1;30(2):186-214. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmad029. Hum Reprod Update. 2024. PMID: 38007607 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists in moderate-to-severe endometriosis-associated pain: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Oct;308(4):1047-1056. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06862-0. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36656435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carr BR. Endometriosis. In: Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, Halvorson LM, Hoffman B, Bradshaw KD, Cunningham FG, eds. Williams Gynecology. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008:chapter 10
-
- Crosignani PG, Luciano A, Ray A, Bergqvist A. Subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate versus leuprolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2006;21 (1):248–256 - PubMed
-
- Schlaff WD, Carson SA, Luciano A, Ross D, Bergqvist A. Subcutaneous injection of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate compared with leuprolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Fertil Steril. 2006;85 (2):314–325 - PubMed
-
- Vercellini P, Fedele L, Pietropaolo G, Frontino G, Somigliana E, Crosignani PG. Progestogens for endometriosis: forward to the past. Hum Reprod Update. 2003;9 (4):387–396 - PubMed
-
- Batzer FR. GnRH analogs: options for endometriosis-associated pain treatment. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2006;13 (6):539–545 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

