Non-metastatic 2 (NME2)-mediated suppression of lung cancer metastasis involves transcriptional regulation of key cell adhesion factor vinculin
- PMID: 25249619
- PMCID: PMC4191424
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku860
Non-metastatic 2 (NME2)-mediated suppression of lung cancer metastasis involves transcriptional regulation of key cell adhesion factor vinculin
Abstract
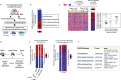
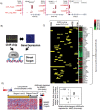
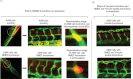
Tumor metastasis refers to spread of a tumor from site of its origin to distant organs and causes majority of cancer deaths. Although >30 metastasis suppressor genes (MSGs) that negatively regulate metastasis have been identified so far, two issues are poorly understood: first, which MSGs oppose metastasis in a tumor type, and second, which molecular function of MSG controls metastasis. Herein, integrative analyses of tumor-transcriptomes (n=382), survival data (n=530) and lymph node metastases (n=100) in lung cancer patients identified non-metastatic 2 (NME2) as a key MSG from a pool of >30 metastasis suppressors. Subsequently, we generated a promoter-wide binding map for NME2 using chromatin immunoprecipitation with promoter microarrays (ChIP-chip), and transcriptome profiling. We discovered novel targets of NME2 which are involved in focal adhesion signaling. Importantly, we detected binding of NME2 in promoter of focal adhesion factor, vinculin. Reduced expression of NME2 led to enhanced transcription of vinculin. In comparison, NME1, a close homolog of NME2, did not bind to vinculin promoter nor regulate its expression. In line, enhanced metastasis of NME2-depleted lung cancer cells was found in zebrafish and nude mice tumor models. The metastatic potential of NME2-depleted cells was remarkably diminished upon selective RNA-i-mediated silencing of vinculin. Together, we demonstrate that reduced NME2 levels lead to transcriptional de-repression of vinculin and regulate lung cancer metastasis.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Fidler I.J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:453–458. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen D.X., Bos P.D., Massague J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009;9:274–284. - PubMed
-
- Gupta G.P., Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

