Chlorophytum borivilianum root extract maintains near normal blood glucose, insulin and lipid profile levels and prevents oxidative stress in the pancreas of streptozotocin-induced adult male diabetic rats
- PMID: 25249786
- PMCID: PMC4166863
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.9056
Chlorophytum borivilianum root extract maintains near normal blood glucose, insulin and lipid profile levels and prevents oxidative stress in the pancreas of streptozotocin-induced adult male diabetic rats
Abstract
The effect of C. borivilianum root on blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbAIc), insulin and lipid profile levels in diabetes mellitus are not fully understood. This study therefore investigated the effect of C. borivilianum root on the above parameters and oxidative stress of the pancreas in diabetes.
Methods: C. borivilianum root aqueous extract (250 and 500 mg/kg/day) was administered to streptozotocin (STZ)-induced male diabetic rats for 28 days. Body weight, blood glucose, HbA1c, insulin, lipid profile levels and glucose homeostasis indices were determined. Histopathological changes and oxidative stress parameters i.e. lipid peroxidation (LPO) and antioxidant enzymes activity levels of the pancreas were investigated.
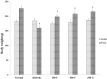
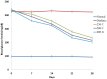
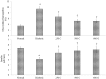
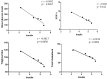
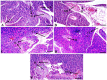
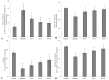
Results: C. borivilianum root extract treatment to diabetic rats maintained near normal body weight, blood glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile and insulin levels with higher HOMA-β cell functioning index, number of Islets/pancreas, number of β-cells/Islets however with lower HOMA-insulin resistance (IR) index as compared to non-treated diabetic rats. Negative correlations between serum insulin and blood glucose, HbA1c, triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) levels were observed. C. borivilianum root extract administration prevented the increase in lipid peroxidation and the decrease in activity levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) with mild histopathological changes in the pancreas of diabetic rats.
Conclusions: C. borivilianum root maintains near normal levels of these metabolites and prevented oxidative stress-induced damage to the pancreas in diabetes.
Keywords: Chlorophytum borivilianum; diabetes; glucose; lipid profile; oxidative stress.; pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors reported no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Packard C, Olsson A. Management of hypercholesterolaemia in the patient with diabetes. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2002:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Gouni-Berthold I, Krone W. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Medizinische Klinik (Munich, Germany: 1983) 2006;101:100–5. - PubMed
-
- Lambrinoudaki I, Tsouvalas E, Vakaki M, Kaparos G, Stamatelopoulos K, Augoulea A. et al. Osteoprotegerin, Soluble Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor- κ B Ligand, and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rajmohan L, Deepa R, Mohan A, Mohan V. Association between isolated hypercholesterolemia, isolated hypertriglyceridemia and coronary artery disease in south Indian type 2 diabetic patients. Indian Heart J. 2000;52:400–6. - PubMed
-
- Khan AS, Latif SU, Eloubeidi MA. Controversies in the etiologies of acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2010;11:545–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

