4-Fluoro-N-(4-hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)aniline
- PMID: 25249910
- PMCID: PMC4158537
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814015153
4-Fluoro-N-(4-hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)aniline
Abstract
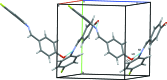
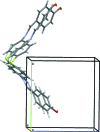
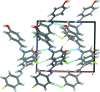
In the title compound, C13H10FNO, the benzene ring planes are inclined at an angle of 50.52 (8)°. A characteristic of aromatic Schiff bases with N-aryl substituents is that the terminal phenyl rings are twisted relative to the plane of the HC=N link between them. In this case, the HC=N unit makes dihedral angles of 10.6 (2) and 40.5 (2)° with the hy-droxy-benzene and fluro-benzene rings, respectively. In the crystal, O-H⋯N and C-H⋯F hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of chains along the c- and b-axis directions, respectively. C-H⋯π contacts link mol-ecules along a and these contacts combine to generate a three-dimensional network with mol-ecules stacked along the b-axis direction.
Keywords: crystal structure.
Figures



References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammeer, L. & Orpen, A. G. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT-Plus, XPREP and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
