4-[(5-Bromo-2-hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)amino]-3-ethyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione
- PMID: 25249924
- PMCID: PMC4158482
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814016833
4-[(5-Bromo-2-hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)amino]-3-ethyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione
Abstract
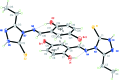
The title compound, C11H11BrN4OS, crystallized as a racemic twin with two symmetry-independent mol-ecules in the asymmetric unit. The dihedral angles between the benzene and triazole rings of the two independent mol-ecules are 56.41 (18) and 54.48 (18)°. An intra-molecular O-H⋯N hydrogen bond occurs in each mol-ecule. In the crystal, pairs of symmetry-independent mol-ecules are linked by pairs of almost linear N-H⋯S hydrogen bonds, forming cyclic dimers characterized by an R 2 (2)(8) motif. There are weak π-π inter-actions between the benzene rings of symmetry-independent mol-ecules, with a centroid-centroid distance of 3.874 (3) Å.
Keywords: crystal structure.
Figures

References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orapen, G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2000). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Demirbas, N. (2004). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 39, 793–804. - PubMed
-
- Demirbas, A., Sahin, D., Demirbas, N. & Alpay-Karaoglu, S. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 2896–2903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
