Transcription factors Foxa1 and Foxa2 are required for adult dopamine neurons maintenance
- PMID: 25249938
- PMCID: PMC4158790
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00275
Transcription factors Foxa1 and Foxa2 are required for adult dopamine neurons maintenance
Abstract
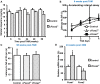
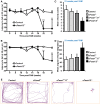
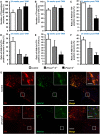
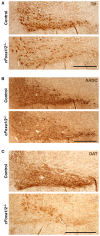
The proteins Foxa1 and Foxa2 belong to the forkhead family of transcription factors and are involved in the development of several tissues, including liver, pancreas, lung, prostate, and the neural system. Both Foxa1 and Foxa2 are also crucial for the specification and differentiation of dopamine (DA) neurons during embryonic development, while about 30% of mice with an embryonic deletion of a single allele of the Foxa2 gene exhibit an age-related asymmetric loss of DA neurons and develop locomotor symptoms resembling Parkinson's disease (PD). Notably, both Foxa1 and Foxa2 factors continue to be expressed in the adult dopamine system. To directly assess their functions selectively in adult DA neurons, we induced genetic deletions of Foxa1/2 transcription factors in mice using a tamoxifen inducible tissue-specific CreERT2 recombinase expressed under control of the dopamine transporter (DAT) promoter (DATCreERT2). The conditional DA neurons-specific ablation of both genes, but not of Foxa2 alone, in early adulthood, caused a decline of striatal dopamine and its metabolites, along with locomotor deficits. At early pre-symptomatic stages, we observed a decline in aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1, subfamily A1 (Aldh1a1) protein expression in DA neurons. Further analyses revealed a decline of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) and a complete loss of DAT expression in these neurons. These molecular changes ultimately led to a reduction of DA neuron numbers in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) of aged cFoxa1/2 (-/-) mice, resembling the progressive course of PD in humans. Altogether, in this study, we address the molecular, cellular, and functional role of both Foxa1 and Foxa2 factors in the maintenance of the adult dopamine system which may help to find better approaches for PD treatment.
Keywords: Foxa1; Foxa2; Parkinson's disease; dopamine; dopaminergic neurons; neurodegeneration; substantia nigra; transgenic mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription factors FOXA1 and FOXA2 maintain dopaminergic neuronal properties and control feeding behavior in adult mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 1;112(35):E4929-38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503911112. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26283356 Free PMC article.
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 function both upstream of and cooperatively with Lmx1a and Lmx1b in a feedforward loop promoting mesodiencephalic dopaminergic neuron development.Dev Biol. 2009 Sep 15;333(2):386-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.07.006. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19607821
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 regulate multiple phases of midbrain dopaminergic neuron development in a dosage-dependent manner.Development. 2007 Aug;134(15):2761-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.000141. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Development. 2007. PMID: 17596284
-
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 making molecular inroads into the differential vulnerability of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron subtypes in Parkinson's disease.Transl Neurodegener. 2014 Dec 10;3:27. doi: 10.1186/2047-9158-3-27. eCollection 2014. Transl Neurodegener. 2014. PMID: 25705376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine transporter: involvement in selective dopaminergic neurotoxicity and degeneration.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2004 Oct;111(10-11):1267-86. doi: 10.1007/s00702-004-0203-2. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2004. PMID: 15480838 Review.
Cited by
-
Common genetic variants associated with Parkinson's disease display widespread signature of epigenetic plasticity.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 5;9(1):18464. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54865-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31804560 Free PMC article.
-
Foxa1 is essential for development and functional integrity of the subthalamic nucleus.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 9;6:38611. doi: 10.1038/srep38611. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27934886 Free PMC article.
-
Embryoid Body Cells from Human Embryonic Stem Cells Overexpressing Dopaminergic Transcription Factors Survive and Initiate Neurogenesis via Neural Rosettes in the Substantia Nigra.Brain Sci. 2023 Feb 14;13(2):329. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020329. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36831872 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease: Overview of Transcription Factor Regulation, Genetics, and Cellular and Animal Models.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 4;16:894620. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.894620. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35600613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular plasticity and the neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 May;15(5):271-286. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2018.22. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 29460922 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

