The lethal cargo of Myxococcus xanthus outer membrane vesicles
- PMID: 25250022
- PMCID: PMC4158809
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00474
The lethal cargo of Myxococcus xanthus outer membrane vesicles
Abstract
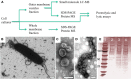
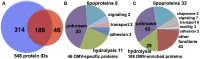
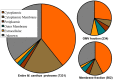
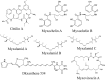
Myxococcus xanthus is a bacterial micro-predator known for hunting other microbes in a wolf pack-like manner. Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are produced in large quantities by M. xanthus and have a highly organized structure in the extracellular milieu, sometimes occurring in chains that link neighboring cells within a biofilm. OMVs may be a vehicle for mediating wolf pack activity by delivering hydrolytic enzymes and antibiotics aimed at killing prey microbes. Here, both the protein and small molecule cargo of the OMV and membrane fractions of M. xanthus were characterized and compared. Our analysis indicates a number of proteins that are OMV-specific or OMV-enriched, including several with putative hydrolytic function. Secondary metabolite profiling of OMVs identifies 16 molecules, many associated with antibiotic activities. Several hydrolytic enzyme homologs were identified, including the protein encoded by MXAN_3564 (mepA), an M36 protease homolog. Genetic disruption of mepA leads to a significant reduction in extracellular protease activity suggesting MepA is part of the long-predicted (yet to date undetermined) extracellular protease suite of M. xanthus.
Keywords: fruiting body; predation; predator-prey interactions; predatory rippling; secondary metabolism and enzymes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predatory Strategies of Myxococcus xanthus: Prey Susceptibility to OMVs and Moonlighting Enzymes.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 29;11(4):874. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11040874. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37110297 Free PMC article.
-
Predatory activity of Myxococcus xanthus outer-membrane vesicles and properties of their hydrolase cargo.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Nov;158(Pt 11):2742-2752. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.060343-0. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22977088
-
Within-species variation in OMV cargo proteins: the Myxococcus xanthus OMV pan-proteome.Mol Omics. 2020 Aug 1;16(4):387-397. doi: 10.1039/d0mo00027b. Epub 2020 May 6. Mol Omics. 2020. PMID: 32373862
-
The predatory life cycle of Myxococcus xanthus.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Jan;162(1):1-11. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000208. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 26518442 Review.
-
Myxobacterial vesicles death at a distance?Adv Appl Microbiol. 2011;75:1-31. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387046-9.00001-3. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21807244 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Functions Affecting Predator-Prey Interactions between Myxococcus xanthus and Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2016 Nov 18;198(24):3335-3344. doi: 10.1128/JB.00575-16. Print 2016 Dec 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27698086 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;13:835058. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.835058. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35283837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kin discrimination and outer membrane exchange in Myxococcus xanthus: Experimental analysis of a natural population.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 27;14(11):e0224817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224817. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31774841 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilms with bacterial-derived outer membrane vesicles.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Aug 24;21(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02296-x. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34429066 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as an Efficient and Versatile System for Drug Delivery.Cells. 2020 Sep 29;9(10):2191. doi: 10.3390/cells9102191. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33003285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

