Peptide targeted high-resolution molecular imaging of prostate cancer with MRI
- PMID: 25250202
- PMCID: PMC4171839
Peptide targeted high-resolution molecular imaging of prostate cancer with MRI
Abstract
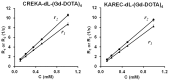
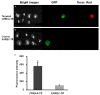
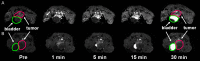
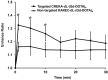
Non-invasive accurate detection of prostate cancer is critical for clinical management of the disease. Molecular MRI has a potential for accurate detection of prostate cancer with high spatial resolution. Fibronectin is a hallmark of epithelial-mesenchymal transition occurred in aggressive prostate cancer and highly expressed in malignant tumors. A pentapeptide CREKA targeted contrast agent CREKA-dL-(DOTA-Gd)4 was synthesized and evaluated to target fibrin-fibronectin complexes in tumor extracellular matrix for molecular MRI of prostate cancer. The contrast agent was synthesized by solid-phase peptide synthesis. The T1 relaxivity of CREKA-(DOTA-Gd)4 at 1.5 T was 33.2 mM(-1)s(-1) per molecule (8.3 per Gd). The fluorescence imaging showed that CREKA specifically bound to orthotopic PC3 prostate tumor in athymic nude mice. Strong enhancement was observed in the tumor tissue injected with CREKA-(DOTA-Gd)4 in the first 5 minutes post-injection before MR signal became visible in the bladder at a low dose of 0.03 mmol-Gd/kg. The targeted contrast agent exhibited minimal Gd retention in the main organs and tissues 2 days after injection. The peptide targeted contrast agent CREKA-(DOTA-Gd)4 is promising for high-resolution molecular MRI of prostate cancer.
Keywords: MRI; Molecular imaging; peptide; prostate cancer; targeted contrast agent.
Figures


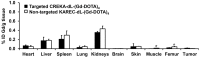
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Shah RB. Current perspectives on the Gleason grading of prostate cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1810–1816. - PubMed
-
- Durmus T, Reichelt U, Huppertz A, Hamm B, Beyersdorff D, Franiel T. MRI-guided biopsy of the prostate: correlation between the cancer detection rate and the number of previous negative TRUS biopsies. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19:411–417. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
