Proteomics analysis for finding serum markers of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 25250314
- PMCID: PMC4164372
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/179040
Proteomics analysis for finding serum markers of ovarian cancer
Abstract
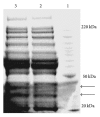
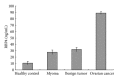
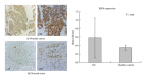
A combination of peptide ligand library beads (PLLB) and 1D gel liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (1DGel-LC-MS/MS) was employed to analyze serum samples from patients with ovarian cancer and from healthy controls. Proteomic analysis identified 1200 serum proteins, among which 57 proteins were upregulated and 10 were downregulated in the sera from cancer patients. Retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) is highly upregulated in the ovarian cancer serum samples. ELISA was employed to measure plasma concentrations of RBP4 in 80 samples from ovarian cancer patients, healthy individuals, myoma patients, and patients with benign ovarian tumor, respectively. The plasma concentrations of RBP4 ranging from 76.91 to 120.08 ng/mL with the mean value 89.13 ± 1.67 ng/mL in ovarian cancer patients are significantly higher than those in healthy individuals (10.85 ± 2.38 ng/mL). Results were further confirmed with immunohistochemistry, demonstrating that RBP4 expression levels in normal ovarian tissue were lower than those in ovarian cancer tissues. Our results suggested that RBP4 is a potential biomarker for diagnostic of screening ovarian cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased concentrations of retinol-binding protein 4 in sera of epithelial ovarian cancer patients: a potential biomarker identified by proteomics.Oncol Rep. 2012 Feb;27(2):318-24. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1513. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22020625
-
Discovery of serum biomarkers of ovarian cancer using complementary proteomic profiling strategies.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014 Dec;8(11-12):982-93. doi: 10.1002/prca.201400063. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014. PMID: 25290619 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of proteomics-identified CCL18 and CXCL1 as circulating tumor markers for differential diagnosis between ovarian carcinomas and benign pelvic masses.Int J Biol Markers. 2011 Oct-Dec;26(4):262-73. doi: 10.5301/JBM.2011.8616. Int J Biol Markers. 2011. PMID: 21928244
-
Proteomic analysis for early detection of ovarian cancer: a realistic approach?Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003 Nov-Dec;13 Suppl 2:133-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2003.13358.x. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14656269 Review.
-
Translational Research and Plasma Proteomic in Cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Apr;117(4):828-35. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25413. Epub 2015 Dec 8. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26479787 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Vinculin as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Acute Aortic Dissection Using Label-Free Proteomics.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 19;2020:7806409. doi: 10.1155/2020/7806409. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32766314 Free PMC article.
-
Adipokine RBP4 drives ovarian cancer cell migration.J Ovarian Res. 2018 Apr 11;11(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0397-9. J Ovarian Res. 2018. PMID: 29642915 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of 2DE Patterns of Plasma Proteins: Aspect of Potential Tumor Markers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;23(19):11113. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911113. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232415 Free PMC article.
-
Tubulin Beta 2C Chain (TBB2C), a Potential Marker of Ovarian Cancer, an Insight from Ovarian Cancer Proteome Profile.ACS Omega. 2021 Apr 13;6(16):10506-10514. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03262. eCollection 2021 Apr 27. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34056205 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Ovarian Endometrioma and Its Possible Role in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 29;22(11):5827. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115827. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scully RE, Young RH, Clement PB. Tumors of the ovary, maldeveloped gonads, fallopian tube, and broad ligament. Atlas of Tumor Pathology. 1998;3:p. 228.
-
- Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975–2002. National Cancer Institute; 2005.
-
- Jemal A, Clegg L, Ward E, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2001, with a special feature regardin survival. Cancer. 2004;101(1):3–27. - PubMed
-
- Tiffen J, Mahon SM. Ovarian cancer screening: are there any options? Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing. 2005;9(3):369–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

