Phase 2 study of RO4929097, a gamma-secretase inhibitor, in metastatic melanoma: SWOG 0933
- PMID: 25250858
- PMCID: PMC4304973
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.29055
Phase 2 study of RO4929097, a gamma-secretase inhibitor, in metastatic melanoma: SWOG 0933
Abstract
Background: Aberrant Notch activation confers a proliferative advantage to many human tumors, including melanoma. This phase 2 trial assessed the antitumor activity of RO4929097, a gamma-secretase inhibitor of Notch signaling, with respect to the progression-free and overall survival of patients with advanced melanoma.
Methods: Chemotherapy-naive patients with metastatic melanoma of cutaneous or unknown origin were treated orally with RO4929097 at a dose of 20 mg daily 3 consecutive days per week. A 2-step accrual design was used with an interim analysis of the first 32 patients and with continuation of enrollment if 4 or more of the 32 patients responded.
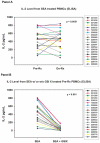
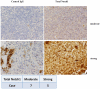
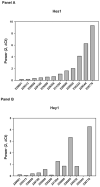
Results: Thirty-six patients from 23 institutions were enrolled; 32 patients were evaluable. RO4929097 was well tolerated, and most toxicities were grade 1 or 2. The most common toxicities were nausea (53%), fatigue (41%), and anemia (22%). There was 1 confirmed partial response lasting 7 months, and there were 8 patients with stable disease lasting at least through week 12, with 1 of these continuing for 31 months. The 6-month progression-free survival rate was 9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 2%-22%), and the 1-year overall survival rate was 50% (95% CI, 32%-66%). Peripheral blood T-cell assays showed no significant inhibition of the production of interleukin-2, a surrogate pharmacodynamic marker of Notch inhibition, and this suggested that the drug levels were insufficient to achieve Notch target inhibition.
Conclusions: RO4929097 showed minimal clinical activity against metastatic melanoma in this phase 2 trial, possibly because of inadequate exposure to therapeutic drug levels. Although Notch inhibition remains a compelling target in melanoma, the results do not support further investigation of RO4929097 with this dose and schedule.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01120275.
Keywords: Notch; RO4929097; gamma-secretase inhibitor; metastatic melanoma.
© 2014 American Cancer Society.
Figures



References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999 Apr 30;284(5415):770–776. - PubMed
-
- Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, et al. Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science. 2004 Oct 8;306(5694):269–271. - PubMed
-
- Leong KG, Karsan A. Recent insights into the role of Notch signaling in tumorigenesis. Blood. 2006 Mar 15;107(6):2223–2233. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Schaider H, Satyamoorthy K, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Herlyn M. Downregulation of E-cadherin and Desmoglein 1 by autocrine hepatocyte growth factor during melanoma development. Oncogene. 2001 Dec 6;20(56):8125–8135. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann JM, Holzmann B, Breitbart EW, Schmiegelow P, Riethmuller G, Johnson JP. Discrimination between benign and malignant cells of melanocytic lineage by two novel antigens, a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 113,000 and a protein with a molecular weight of 76,000. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):841–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128567/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA174664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA128567/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA095860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA068183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

