Safety assessment of liver-targeted hydrodynamic gene delivery in dogs
- PMID: 25251246
- PMCID: PMC4175463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107203
Safety assessment of liver-targeted hydrodynamic gene delivery in dogs
Abstract
Evidence in support of safety of a gene delivery procedure is essential toward gene therapy. Previous studies using the hydrodynamics-based procedure primarily focus on gene delivery efficiency or gene function analysis in mice. The current study focuses on an assessment of the safety of computer-controlled and liver-targeted hydrodynamic gene delivery in dogs as the first step toward hydrodynamic gene therapy in clinic. We demonstrate that the impacts of the hydrodynamic procedure were limited in the injected region and the influences were transient. Histological examination and the hepatic microcirculation measurement using reflectance spectrophotometry reveal that the liver-specific impact of the procedure involves a transient expansion of the liver sinusoids. No systemic damage or toxicity was observed. Physiological parameters, including electrocardiogram, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and body temperature, remained in normal ranges during and after hydrodynamic injection. Body weight was also examined to assess the long-term effects of the procedure in animals who underwent 3 hydrodynamic injections in 6 weeks with 2-week time interval in between. Serum biochemistry analysis showed a transient increase in liver enzymes and a few cytokines upon injection. These results demonstrate that image-guided, liver-specific hydrodynamic gene delivery is safe.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
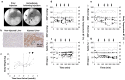
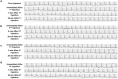


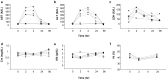
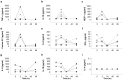
References
-
- Ginn SL, Alexander IE, Edelstein ML, Abedi MR, Wixon J (2013) Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2012 - an update. J Gene Med 15: 65–77. - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Song Y, Liu D (1999) Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther 6: 1258–1266. - PubMed
-
- Zhang G, Budker V, Wolff JA (1999) High levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum Gene Ther 10: 1735–1737. - PubMed
-
- Suda T, Liu D (2007) Hydrodynamic gene delivery: its principles and applications. Mol Ther 15: 2063–2069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

