Role of microRNAs in arbovirus/vector interactions
- PMID: 25251636
- PMCID: PMC4189037
- DOI: 10.3390/v6093514
Role of microRNAs in arbovirus/vector interactions
Abstract
The role of microRNAs (miRNAs) as small non-coding RNAs in regulation of gene expression has been recognized. They appear to be involved in regulation of a wide range of cellular pathways that affect several biological processes such as development, the immune system, survival, metabolism and host-pathogen interactions. Arthropod-borne viruses impose great economic and health risks around the world. Recent advances in miRNA biology have shed some light on the role of these small RNAs in vector-virus interactions. In this review, I will reflect on our current knowledge on the role of miRNAs in arbovirus-vector interactions and the potential avenues for their utilization in limiting virus replication and/or transmission.
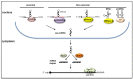
Figures

References
-
- Turell M.J. Arthropod-Related viruses of medical and veterinary importance. In: Mullen G., Durden L., editors. Medical and Veterinary Entomology. Academic Press; Oxford, UK: 2009. pp. 557–564.
-
- Landthaler M., Yalcin A., Tuschl T. The human DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 and its D. melanogaster homolog are required for miRNA biogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:2162–2167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

