Regulation of transcription by long noncoding RNAs
- PMID: 25251851
- PMCID: PMC4285387
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092323
Regulation of transcription by long noncoding RNAs
Abstract
Over the past decade there has been a greater understanding of genomic complexity in eukaryotes ushered in by the immense technological advances in high-throughput sequencing of DNA and its corresponding RNA transcripts. This has resulted in the realization that beyond protein-coding genes, there are a large number of transcripts that do not encode for proteins and, therefore, may perform their function through RNA sequences and/or through secondary and tertiary structural determinants. This review is focused on the latest findings on a class of noncoding RNAs that are relatively large (>200 nucleotides), display nuclear localization, and use different strategies to regulate transcription. These are exciting times for discovering the biological scope and the mechanism of action for these RNA molecules, which have roles in dosage compensation, imprinting, enhancer function, and transcriptional regulation, with a great impact on development and disease.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; chromatin; chromatin-modifying complexes; enhancers; imprinting; transcriptional silencing.
Figures
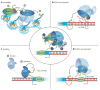


References
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D. Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harb. Lab. Press; 2007. p. 502.
-
- Amrein H, Axel R. Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell. 1997;88:459–69. - PubMed
-
- Batish M, Raj A, Tyagi S. Single molecule imaging of RNA in situ. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;714:3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

