Pleiotropic roles of Notch signaling in normal, malignant, and developmental hematopoiesis in the human
- PMID: 25252682
- PMCID: PMC4253487
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201438842
Pleiotropic roles of Notch signaling in normal, malignant, and developmental hematopoiesis in the human
Abstract
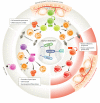
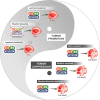
The Notch signaling pathway is evolutionarily conserved across species and plays an important role in regulating cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. It has been implicated in several different hematopoietic processes including early hematopoietic development as well as adult hematological malignancies in humans. This review focuses on recent developments in understanding the role of Notch signaling in the human hematopoietic system with an emphasis on hematopoietic initiation from human pluripotent stem cells and regulation within the bone marrow. Based on recent insights, we summarize potential strategies for treatment of human hematological malignancies toward the concept of targeting Notch signaling for fate regulation.
Keywords: Notch; hematopoiesis; human pluripotent stem cells; leukemia.
© 2014 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, Soreng AL, Reynolds TC, Smith SD, Sklar J. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991;66:649–661. - PubMed
-
- Singh N, Phillips RA, Iscove NN, Egan SE. Expression of notch receptors, notch ligands, and fringe genes in hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 2000;28:527–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

