In vivo disruption of an Rb-E2F-Ezh2 signaling loop causes bladder cancer
- PMID: 25252918
- PMCID: PMC4233185
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1218
In vivo disruption of an Rb-E2F-Ezh2 signaling loop causes bladder cancer
Abstract
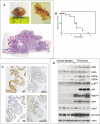
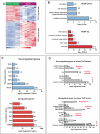
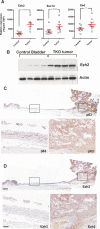
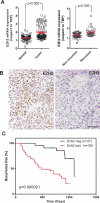
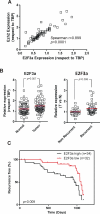
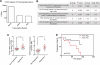
Bladder cancer is a highly prevalent human disease in which retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway inactivation and epigenetic alterations are common events. However, the connection between these two processes is still poorly understood. Here, we show that the in vivo inactivation of all Rb family genes in the mouse urothelium is sufficient to initiate bladder cancer development. The characterization of the mouse tumors revealed multiple molecular features of human bladder cancer, including the activation of E2F transcription factor and subsequent Ezh2 expression and the activation of several signaling pathways previously identified as highly relevant in urothelial tumors. These mice represent a genetically defined model for human high-grade superficial bladder cancer. Whole transcriptional characterizations of mouse and human bladder tumors revealed a significant overlap and confirmed the predominant role for Ezh2 in the downregulation of gene expression programs. Importantly, the increased tumor recurrence and progression in human patients with superficial bladder cancer is associated with increased E2F and Ezh2 expression and Ezh2-mediated gene expression repression. Collectively, our studies provide a genetically defined model for human high-grade superficial bladder cancer and demonstrate the existence of an Rb-E2F-Ezh2 axis in bladder whose disruption can promote tumor development.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Wu X, Hildebrandt MA, Chang DW. Genome-wide association studies of bladder cancer risk: a field synopsis of progress and potential applications. Cancer metastasis reviews. 2009;28:269–80. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher DJ, Milowsky MI. Bladder cancer. Current treatment options in oncology. 2009;10:205–15. - PubMed
-
- Burger M, Oosterlinck W, Konety B, Chang S, Gudjonsson S, Pruthi R, et al. ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012: Non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. European urology. 2013;63:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Knowles MA. Molecular subtypes of bladder cancer: Jekyll and Hyde or chalk and cheese? Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:361–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

