Whole-genome sequencing identifies genetic variances in culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 25254336
- PMCID: PMC4176531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.05.019
Whole-genome sequencing identifies genetic variances in culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
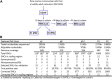
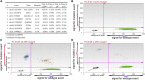
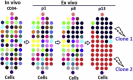
Culture-expanded human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are increasingly used in clinics, yet full characterization of the genomic compositions of these cells is lacking. We present a whole-genome investigation on the genetic dynamics of cultured MSCs under ex vivo establishment (passage 1 [p1]) and serial expansion (p8 and p13). We detected no significant changes in copy-number alterations (CNAs) and low levels of single-nucleotide changes (SNCs) until p8. Strikingly, a significant number (677) of SNCs were found in p13 MSCs. Using a sensitive Droplet Digital PCR assay, we tested the nonsynonymous SNCs detected by whole-genome sequencing and found that they were preexisting low-frequency mutations in uncultured mononuclear cells (∼0.01%) and early-passage MSCs (0.1%-1% at p1 and p8) but reached 17%-36% in p13. Our data demonstrate that human MSCs maintain a stable genomic composition in the early stages of ex vivo culture but are subject to clonal growth upon extended expansion.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

