Fringe proteins modulate Notch-ligand cis and trans interactions to specify signaling states
- PMID: 25255098
- PMCID: PMC4174579
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.02950
Fringe proteins modulate Notch-ligand cis and trans interactions to specify signaling states
Erratum in
- Elife. 2014;3:e04998
Abstract
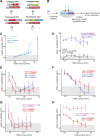
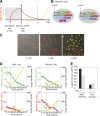
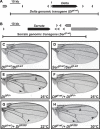
The Notch signaling pathway consists of multiple types of receptors and ligands, whose interactions can be tuned by Fringe glycosyltransferases. A major challenge is to determine how these components control the specificity and directionality of Notch signaling in developmental contexts. Here, we analyzed same-cell (cis) Notch-ligand interactions for Notch1, Dll1, and Jag1, and their dependence on Fringe protein expression in mammalian cells. We found that Dll1 and Jag1 can cis-inhibit Notch1, and Fringe proteins modulate these interactions in a way that parallels their effects on trans interactions. Fringe similarly modulated Notch-ligand cis interactions during Drosophila development. Based on these and previously identified interactions, we show how the design of the Notch signaling pathway leads to a restricted repertoire of signaling states that promote heterotypic signaling between distinct cell types, providing insight into the design principles of the Notch signaling system, and the specific developmental process of Drosophila dorsal-ventral boundary formation.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; cell signaling; developmental biology; developmental patterning; notch pathway; stem cells; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures










References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

