A fluorimetric readout reporting the kinetics of nucleotide-induced human ribonucleotide reductase oligomerization
- PMID: 25256246
- PMCID: PMC4271543
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201402368
A fluorimetric readout reporting the kinetics of nucleotide-induced human ribonucleotide reductase oligomerization
Abstract
Human ribonucleotide reductase (hRNR) is a target of nucleotide chemotherapeutics in clinical use. The nucleotide-induced oligomeric regulation of hRNR subunit α is increasingly being recognized as an innate and drug-relevant mechanism for enzyme activity modulation. In the presence of negative feedback inhibitor dATP and leukemia drug clofarabine nucleotides, hRNR-α assembles into catalytically inert hexameric complexes, whereas nucleotide effectors that govern substrate specificity typically trigger α-dimerization. Currently, both knowledge of and tools to interrogate the oligomeric assembly pathway of RNR in any species in real time are lacking. We therefore developed a fluorimetric assay that reliably reports on oligomeric state changes of α with high sensitivity. The oligomerization-directed fluorescence quenching of hRNR-α, covalently labeled with two fluorophores, allows for direct readout of hRNR dimeric and hexameric states. We applied the newly developed platform to reveal the timescales of α self-assembly, driven by the feedback regulator dATP. This information is currently unavailable, despite the pharmaceutical relevance of hRNR oligomeric regulation.
Keywords: feedback inhibition; fluorescence reporter assay; human ribonucleotide reductase; oligomeric regulation; stopped-flow kinetics.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


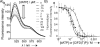



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

