Ultra-sensitive immunoassay biosensors using hybrid plasmonic-biosilica nanostructured materials
- PMID: 25256544
- PMCID: PMC4758816
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201400070
Ultra-sensitive immunoassay biosensors using hybrid plasmonic-biosilica nanostructured materials
Abstract
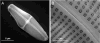
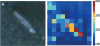
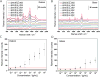
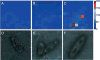
We experimentally demonstrate an ultra-sensitive immunoassay biosensor using diatom biosilica with self-assembled plasmonic nanoparticles. As the nature-created photonic crystal structures, diatoms have been adopted to enhance surface plasmon resonances of metal nanoparticles on the surfaces of diatom frustules and to increase the sensitivity of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). In this study, a sandwich SERS immunoassay is developed based on the hybrid plasmonic-biosilica nanostructured materials that are functionalized with goat anti-mouse IgG. Our experimental results show that diatom frustules improve the detection limit of mouse IgG to 10 pg/mL, which is ˜100× better than conventional colloidal SERS sensors on flat glass. Ultra-sensitive immunoassay biosensor using diatom biosilica with self-assembled plasmonic nanoparticles.
Keywords: diatom biosilica; immunoassay; photonic crystal; surface plasmon; surface-enhanced Raman scattering.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Rusmini F, Zhong ZY, Feijen J. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:1775. - PubMed
-
- Lequin RM. Clinical Chemistry. 2005;51:2415. - PubMed
-
- Riboh JC, Haes AJ, McFarland AD, Yonzon CR, Van Duyne RP. Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 2003;107:1772.
-
- Kreisig T, Hoffmann R, Zuchner T. Analytical Chemistry. 2011;83:4281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

