Biologic-free remission of established rheumatoid arthritis after discontinuation of abatacept: a prospective, multicentre, observational study in Japan
- PMID: 25257039
- PMCID: PMC4372674
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu338
Biologic-free remission of established rheumatoid arthritis after discontinuation of abatacept: a prospective, multicentre, observational study in Japan
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine whether biologic-free remission of RA is possible with discontinuation of abatacept.
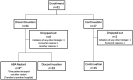
Methods: Japanese RA patients in 28-joint DAS with CRP (DAS28-CRP) remission (<2.3) after >2 years of abatacept treatment in a phase II study and its long-term extension entered this 52 week, multicentre, non-blinded, prospective, observational study. At enrolment, the patients were offered the option to continue abatacept or not. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who remained biologic-free at 52 weeks after discontinuation. Clinical, functional and structural outcomes were compared between those who continued and those who discontinued abatacept.
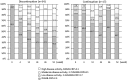
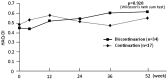
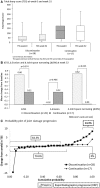
Results: Of 51 patients enrolled, 34 discontinued and 17 continued abatacept treatment. After 52 weeks, 22 of the 34 patients (64.7%) remained biologic-free. Compared with the continuation group, the discontinuation group had a similar remission rate (41.2% vs 64.7%, P = 0.144) although they had a significantly higher mean DAS28-CRP score at week 52 (2.9 vs 2.0, P = 0.012). The two groups were also similar with regard to mean HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score (0.6 for both, P = 0.920), mean change in total Sharp score (ΔTSS; 0.80 vs 0.32, P = 0.374) and proportion of patients in radiographic remission (ΔTSS ≤ 0.5) at the endpoint (64.3% vs 70.6%, P = 0.752). Those attaining DAS28-CRP < 2.3 or < 2.7 without abatacept at the endpoint had significantly lower HAQ-DI score and/or CRP at enrolment. Non-serious adverse events occurred in three patients who continued or resumed abatacept.
Conclusion: Biologic-free remission of RA is possible in some patients after attaining clinical remission with abatacept. Lower baseline HAQ-DI or CRP may predict maintenance of remission or low disease activity after discontinuation of abatacept.
Trial registration: UMIN Clinical Trials Registry, http://www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/ (UMIN000004137).
Keywords: abatacept; biologic-free remission; observational study; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Greater remission rates in patients with early versus long-standing disease in biologic-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with abatacept: a post hoc analysis of randomized clinical trial data.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011 May-Jun;29(3):494-9. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21722499 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating drug-free remission with abatacept in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from the phase 3b, multicentre, randomised, active-controlled AVERT study of 24 months, with a 12-month, double-blind treatment period.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74(1):19-26. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206106. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25367713 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Differences in Predictive Factors for Sustained Clinical Remission with Abatacept Between Younger and Elderly Patients with Biologic-naive Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the ABROAD Study.J Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;43(11):1974-1983. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.160051. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27585689
-
Indirect treatment comparison of abatacept with methotrexate versus other biologic agents for active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy in the United kingdom.J Rheumatol. 2012 Jun;39(6):1198-206. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111345. Epub 2012 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22505698 Review.
-
Evaluation of abatacept in biologic-naïve patients with active rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Jun;29(6):583-91. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1363-0. Epub 2010 Jan 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20099018 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose reduction of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis achieving sustained disease control: results of a prospective study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Feb;78(2):171-178. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213271. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30194275 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment Patterns of Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs and Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Japan: A Claims-Based Cohort Study.Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2024 Jun;11(2):285-297. doi: 10.1007/s40801-024-00423-4. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 38598110 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab discontinuation after attaining remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who were treated with tocilizumab alone or in combination with methotrexate: results from a prospective randomised controlled study (the second year of the SURPRISE study).Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Sep;77(9):1268-1275. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213416. Epub 2018 May 31. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29853455 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mental health, fatigue and function are associated with increased risk of disease flare following TNF inhibitor tapering in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an exploratory analysis of data from the Optimizing TNF Tapering in RA (OPTTIRA) trial.RMD Open. 2018 May 17;4(1):e000676. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000676. eCollection 2018. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 29862047 Free PMC article.
-
Little Evidence for Usefulness of Biomarkers for Predicting Successful Dose Reduction or Discontinuation of a Biologic Agent in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Feb;69(2):301-308. doi: 10.1002/art.39946. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27696778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ranheim EA, Kipps TJ. Elevated expression of CD80 (B7/BB1) and other accessory molecules on synovial fluid mononuclear cell subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:1637–46. - PubMed
-
- Salomon B, Bluestone JA. Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225–52. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs JD. Therapeutic T-cell manipulation in rheumatoid arthritis: past, present and future. Rheumatology. 2008;47:1461–8. - PubMed
-
- Moreland LW, Alten R, Van den Bosch F, et al. Costimulatory blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot, dose-finding, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating CTLA-4Ig and LEA29Y eighty-five days after the first infusion. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1470–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous