PACAP38 differentially effects genes and CRMP2 protein expression in ischemic core and penumbra regions of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion model mice brain
- PMID: 25257527
- PMCID: PMC4200817
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms150917014
PACAP38 differentially effects genes and CRMP2 protein expression in ischemic core and penumbra regions of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion model mice brain
Abstract
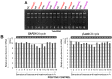
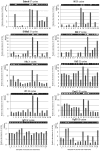
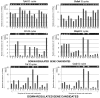
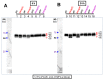
Pituitary adenylate-cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) has neuroprotective and axonal guidance functions, but the mechanisms behind such actions remain unclear. Previously we examined effects of PACAP (PACAP38, 1 pmol) injection intracerebroventrically in a mouse model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (PMCAO) along with control saline (0.9% NaCl) injection. Transcriptomic and proteomic approaches using ischemic (ipsilateral) brain hemisphere revealed differentially regulated genes and proteins by PACAP38 at 6 and 24 h post-treatment. However, as the ischemic hemisphere consisted of infarct core, penumbra, and non-ischemic regions, specificity of expression and localization of these identified molecular factors remained incomplete. This led us to devise a new experimental strategy wherein, ischemic core and penumbra were carefully sampled and compared to the corresponding contralateral (healthy) core and penumbra regions at 6 and 24 h post PACAP38 or saline injections. Both reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blotting were used to examine targeted gene expressions and the collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) protein profiles, respectively. Clear differences in expression of genes and CRMP2 protein abundance and degradation product/short isoform was observed between ischemic core and penumbra and also compared to the contralateral healthy tissues after PACAP38 or saline treatment. Results indicate the importance of region-specific analyses to further identify, localize and functionally analyse target molecular factors for clarifying the neuroprotective function of PACAP38.
Figures

References
-
- Gusev E.I., Skvortsova V.I. Brain Ischemia. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York, NY, USA: 2003.
-
- Kimura C., Ohkubo S., Ogi K., Hosoya M., Itoh Y., Onda H., Miyata A., Jian L., Dahl R.R., Stibbs H.H., et al. A novel peptide which stimulates adenylate cyclase: Molecular cloning and characterization of the ovine and human cDNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990;166:81–89. - PubMed
-
- Arimura A. Perspectives on pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) in the neuroendocrine, endocrine, and nervous systems. Jpn. J. Physiol. 1998;48:301–331. - PubMed
-
- Shioda S., Ozawa H., Dohi K., Mizushima H., Matsumoto K., Nakajo S., Takaki A., Zhou C.J., Nakai Y., Arimura A. PACAP protects hippocampal neurons against apoptosis: Involvement of JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998;865:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Ohtaki H., Funahashi H., Dohi K., Oguro T., Horai R., Asano M., Iwakura Y., Yin L., Matsunaga M., Goto N., et al. Suppression of oxidative neuronal damage after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice lacking interleukin-1. Neurosci. Res. 2003;45:313–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

