Ultra-high-field MR imaging in polymicrogyria and epilepsy
- PMID: 25258368
- PMCID: PMC5548091
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A4116
Ultra-high-field MR imaging in polymicrogyria and epilepsy
Abstract
Background and purpose: Polymicrogyria is a malformation of cortical development that is often identified in children with epilepsy or delayed development. We investigated in vivo the potential of 7T imaging in characterizing polymicrogyria to determine whether additional features could be identified.
Materials and methods: Ten adult patients with polymicrogyria previously diagnosed by using 3T MR imaging underwent additional imaging at 7T. We assessed polymicrogyria according to topographic pattern, extent, symmetry, and morphology. Additional imaging sequences at 7T included 3D T2* susceptibility-weighted angiography and 2D tissue border enhancement FSE inversion recovery. Minimum intensity projections were used to assess the potential of the susceptibility-weighted angiography sequence for depiction of cerebral veins.
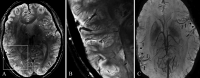
Results: At 7T, we observed perisylvian polymicrogyria that was bilateral in 6 patients, unilateral in 3, and diffuse in 1. Four of the 6 bilateral abnormalities had been considered unilateral at 3T. While 3T imaging revealed 2 morphologic categories (coarse, delicate), 7T susceptibility-weighted angiography images disclosed a uniform ribbonlike pattern. Susceptibility-weighted angiography revealed numerous dilated superficial veins in all polymicrogyric areas. Tissue border enhancement imaging depicted a hypointense line corresponding to the gray-white interface, providing a high definition of the borders and, thereby, improving detection of the polymicrogyric cortex.
Conclusions: 7T imaging reveals more anatomic details of polymicrogyria compared with 3T conventional sequences, with potential implications for diagnosis, genetic studies, and surgical treatment of associated epilepsy. Abnormalities of cortical veins may suggest a role for vascular dysgenesis in pathogenesis.
© 2015 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures


References
-
- Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, et al. . A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 2005;65:1873–87 - PubMed
-
- Harding B, Copp AJ. Malformations. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL, eds. Greenfield's Neuropathology. 6th ed. London: Arnold; 1997:397–533
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
