PCSK9 inhibition fails to alter hepatic LDLR, circulating cholesterol, and atherosclerosis in the absence of ApoE
- PMID: 25258384
- PMCID: PMC4617138
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M053207
PCSK9 inhibition fails to alter hepatic LDLR, circulating cholesterol, and atherosclerosis in the absence of ApoE
Abstract
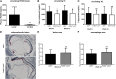
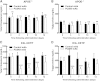
LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) contributes to coronary heart disease. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) increases LDL-C by inhibiting LDL-C clearance. The therapeutic potential for PCSK9 inhibitors is highlighted by the fact that PCSK9 loss-of-function carriers exhibit 15-30% lower circulating LDL-C and a disproportionately lower risk (47-88%) of experiencing a cardiovascular event. Here, we utilized pcsk9(-/-) mice and an anti-PCSK9 antibody to study the role of the LDL receptor (LDLR) and ApoE in PCSK9-mediated regulation of plasma cholesterol and atherosclerotic lesion development. We found that circulating cholesterol and atherosclerotic lesions were minimally modified in pcsk9(-/-) mice on either an LDLR- or ApoE-deficient background. Acute administration of an anti-PCSK9 antibody did not reduce circulating cholesterol in an ApoE-deficient background, but did reduce circulating cholesterol (-45%) and TGs (-36%) in APOE*3Leiden.cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) mice, which contain mouse ApoE, human mutant APOE3*Leiden, and a functional LDLR. Chronic anti-PCSK9 antibody treatment in APOE*3Leiden.CETP mice resulted in a significant reduction in atherosclerotic lesion area (-91%) and reduced lesion complexity. Taken together, these results indicate that both LDLR and ApoE are required for PCSK9 inhibitor-mediated reductions in atherosclerosis, as both are needed to increase hepatic LDLR expression.
Keywords: anti-proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 antibody; apolipoprotein E; low density lipoprotein receptor; proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Steinberg D. 2004. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. An interpretive history of the cholesterol controversy: part I. J. Lipid Res. 45: 1583–1593. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg D. 2005. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. An interpretive history of the cholesterol controversy: part II: the early evidence linking hypercholesterolemia to coronary disease in humans. J. Lipid Res. 46: 179–190. - PubMed
-
- Maxfield F. R., Tabas I. 2005. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 438: 612–621. - PubMed
-
- Gylling H. 2004. Cholesterol metabolism and its implications for therapeutic interventions in patients with hypercholesterolaemia. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 58: 859–866. - PubMed
-
- Top B., Koeleman B. P., Gevers Leuven J. A., Havekes L. M., Frants R. R. 1990. Rearrangements in the LDL receptor gene in Dutch familial hypercholesterolemic patients and the presence of a common 4 kb deletion. Atherosclerosis. 83: 127–136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

