Unraveling the complex relationship triad between lipids, obesity, and inflammation
- PMID: 25258478
- PMCID: PMC4166426
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/502749
Unraveling the complex relationship triad between lipids, obesity, and inflammation
Abstract
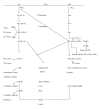
Obesity today stands at the intersection between inflammation and metabolic disorders causing an aberration of immune activity, and resulting in increased risk for diabetes, atherosclerosis, fatty liver, and pulmonary inflammation to name a few. Increases in mortality and morbidity in obesity related inflammation have initiated studies to explore different lipid mediated molecular pathways of attempting resolution that uncover newer therapeutic opportunities of anti-inflammatory components. Majorly the thromboxanes, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, lipoxins, and so forth form the group of lipid mediators influencing inflammation. Of special mention are the omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids that regulate inflammatory mediators of interest in hepatocytes and adipocytes via the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways. They also exhibit profound effects on eicosanoid production. The inflammatory cyclooxygenase pathway arising from arachidonic acid is a critical step in the progression of inflammatory responses. New oxygenated products of omega-3 metabolism, namely, resolvins and protectins, behave as endogenous mediators exhibiting powerful anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory actions via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). In this review we attempt to discuss the complex pathways and links between obesity and inflammation particularly in relation to different lipid mediators.
Figures
References
-
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2006;48(4):677–685. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxins are the first lipid mediators of endogenous anti-inflammation and resolution. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids. 2005;73(3-4):141–162. - PubMed
-
- Nowak JZ. Anti-inflammatory pro-resolving derivatives of omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej. 2010;64:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Wymann MP, Schneiter R. Lipid signalling in disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2008;9(2):162–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

