The current research status of normal tension glaucoma
- PMID: 25258525
- PMCID: PMC4172068
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S67263
The current research status of normal tension glaucoma
Abstract
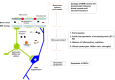
Normal tension glaucoma (NTG) is a progressive optic neuropathy that mimics primary open-angle glaucoma, but lacks the findings of elevated intraocular pressure or other mitigating factors that can lead to optic neuropathy. The present review summarized the causes, genetics, and mechanisms underlying NTG in both animal models and human patients. We also proposed that the neurovascular unit is a therapeutic target for NTG management.
Keywords: aging; genetics; neurovascular unit; primary open-angle glaucoma; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Cantor LB, WuDunn D. 11 Normal-tension glaucoma. In. Color Atlas of Glaucoma. 1998;155
-
- Shields MB. Textbook of glaucoma. Vol. 3. The University of Michigan: Williams & Wilkins; 1998.
-
- Shields MB. Normal-tension glaucoma: is it different from primary open-angle glaucoma? Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19(2):85–88. - PubMed
-
- GLAUCOMA RTOOA. Normal Tension Glaucoma. Primary care of the glaucomas. 2000:113.
-
- Klein BE, Klein R, Sponsel WE, et al. Prevalence of glaucoma. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1992;99(10):1499–1504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

