Time of administration important? Morning versus evening dosing of valsartan
- PMID: 25259546
- PMCID: PMC4284009
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000397
Time of administration important? Morning versus evening dosing of valsartan
Abstract
Objective: Studies suggest that bedtime dosing of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker shows a more sustained and consistent 24-h antihypertensive profile, including greater night-time blood pressure (BP) reduction. We compared the antihypertensive effects of morning (a.m.) and evening (p.m.) dosing of valsartan on 24-h BP.
Methods: This 26-week, multicentre, randomized, double-blind study evaluated the efficacy and safety of valsartan 320 mg, dosed a.m. or p.m., versus lisinopril 40 mg (a.m.), a long-acting ACE-inhibitor, in patients with grade 1-2 hypertension and at least one additional cardiovascular risk factor. Patients (n = 1093; BP = 156 ± 11/91 ± 8 mmHg; 62 years, 56% male, 99% white) received (1 : 1 : 1) valsartan 160 mg a.m. or p.m. or lisinopril 20 mg a.m. for 4 weeks, then force-titrated to double the initial dose for 8 weeks. At Week 12, hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 12.5 mg was added for 14 weeks if office BP was more than 140/90 mmHg and/or ambulatory BP more than 130/80 mmHg.
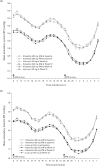
Results: Mean 24-h ambulatory SBP change from baseline to Weeks 12 and 26 was comparable between valsartan a.m. (-10.6 and -13.3 mmHg) and p.m. (-9.8 and -12.3 mmHg) and lisinopril (-10.7 and -13.7 mmHg). There was no benefit of valsartan p.m. versus a.m. on night-time BP, early morning BP and morning BP surge. Evening dosing also did not improve BP lowering in patients requiring add-on HCTZ or in nondippers at baseline. All treatments were well tolerated.
Conclusion: Once-daily dosing of valsartan 320 mg results in equally effective 24-h BP efficacy, regardless of dosing time.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00241124.
Figures
Comment in
-
Should blood pressure medication be taken in the morning or evening?J Hypertens. 2015 Feb;33(2):263-5. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000471. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25535879 No abstract available.
-
Comment on 'Time of administration important? Morning versus evening dosing of valsartan'.J Hypertens. 2015 Mar;33(3):663. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000484. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25629365 No abstract available.
-
Comment on 'Time of administration important? Morning versus evening dosing of valsartan'.J Hypertens. 2015 Mar;33(3):663-4. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000485. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25629366 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anwar YA, White WB. Chronotherapeutics for cardiovascular disease. Drugs 1998; 55:631–643. - PubMed
-
- Gosse P, Lasserre R, Minifié C, Lemetayer P, Clementy J. Blood pressure surge on rising. J Hypertens 2004; 22:1113–1118. - PubMed
-
- Kario K. Vascular damage in exaggerated morning surge in blood pressure. Hypertension 2007; 49:771–772. - PubMed
-
- Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Fernandez JR, Calvo C. Chronotherapy improves blood pressure control and reverts the nondipper pattern in patients with resistant hypertension. Hypertension 2008; 51:69–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous