Environmental stress and epigenetic transgenerational inheritance
- PMID: 25259699
- PMCID: PMC4244059
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-014-0153-y
Environmental stress and epigenetic transgenerational inheritance
Abstract
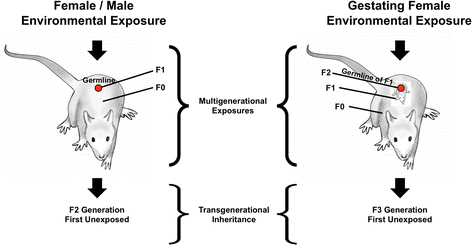
Previous studies have shown a wide variety of environmental toxicants and abnormal nutrition can promote the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease. More recently a number of studies have indicated environmental stress can also promote epigenetic alterations that are transmitted to subsequent generations to induce pathologies. A recent study by Yao and colleagues demonstrated gestational exposure to restraint stress and forced swimming promoted preterm birth risk and adverse newborn outcomes generationally. This ancestral stress promoted the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of abnormalities in the great-grand offspring of the exposed gestating female. Several studies now support the role of environmental stress in promoting the epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease. Observations suggest ancestral environmental stress may be a component of disease etiology in the current population.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical