Melatonin signaling controls circadian swimming behavior in marine zooplankton
- PMID: 25259919
- PMCID: PMC4182423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.042
Melatonin signaling controls circadian swimming behavior in marine zooplankton
Abstract
Melatonin, the "hormone of darkness," is a key regulator of vertebrate circadian physiology and behavior. Despite its ubiquitous presence in Metazoa, the function of melatonin signaling outside vertebrates is poorly understood. Here, we investigate the effect of melatonin signaling on circadian swimming behavior in a zooplankton model, the marine annelid Platynereis dumerilii. We find that melatonin is produced in brain photoreceptors with a vertebrate-type opsin-based phototransduction cascade and a light-entrained clock. Melatonin released at night induces rhythmic burst firing of cholinergic neurons that innervate locomotor-ciliated cells. This establishes a nocturnal behavioral state by modulating the length and the frequency of ciliary arrests. Based on our findings, we propose that melatonin signaling plays a role in the circadian control of ciliary swimming to adjust the vertical position of zooplankton in response to ambient light.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




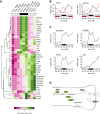
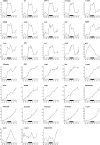


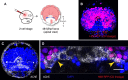

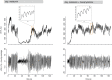

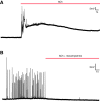
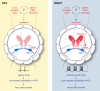
Comment in
-
Deep, dark secrets of melatonin in animal evolution.Cell. 2014 Sep 25;159(1):9-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.004. Cell. 2014. PMID: 25259913
References
-
- Alldredge A.L., King J.M. Effects of moonlight on the vertical migration patterns of demersal zooplankton. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980;44:133–156.
-
- Anctil M., Pani A.K., Ali M.A. Modulation of rhythmic contractions by melatonin via cyclic GMP in the coelenterate Renilla koellikeri. J. Comp. Physiol. B. 1991;161:569–575.
-
- Arendt D., Tessmar-Raible K., Snyman H., Dorresteijn A.W., Wittbrodt J. Ciliary photoreceptors with a vertebrate-type opsin in an invertebrate brain. Science. 2004;306:869–871. - PubMed
-
- Balzer I., Hardeland R. Photoperiodism and effects of indoleamines in a unicellular alga, Gonyaulax polyedra. Science. 1991;253:795–797. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Ackermann C., Dorresteijn A., Fischer A. Clonal domains in postlarval Platynereis dumerilii (Annelida: Polychaeta) J. Morphol. 2005;266:258–280. - PubMed
-
- Anctil M. Chemical transmission in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis: A genomic perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2009;4:268–289. - PubMed
-
- Arendt D., Technau U., Wittbrodt J. Evolution of the bilaterian larval foregut. Nature. 2001;409:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000;17:540–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

