HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data
- PMID: 25260700
- PMCID: PMC4287950
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638
HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data
Abstract
Motivation: A large choice of tools exists for many standard tasks in the analysis of high-throughput sequencing (HTS) data. However, once a project deviates from standard workflows, custom scripts are needed.
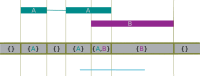
Results: We present HTSeq, a Python library to facilitate the rapid development of such scripts. HTSeq offers parsers for many common data formats in HTS projects, as well as classes to represent data, such as genomic coordinates, sequences, sequencing reads, alignments, gene model information and variant calls, and provides data structures that allow for querying via genomic coordinates. We also present htseq-count, a tool developed with HTSeq that preprocesses RNA-Seq data for differential expression analysis by counting the overlap of reads with genes.
Availability and implementation: HTSeq is released as an open-source software under the GNU General Public Licence and available from http://www-huber.embl.de/HTSeq or from the Python Package Index at https://pypi.python.org/pypi/HTSeq.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Beazley DM, et al. Proceedings of the 4th USENIX Tcl/Tk workshop. 1996. SWIG: an easy to use tool for integrating scripting languages with C and C++ pp. 129–139.
-
- Behnel S, et al. Cython: the best of both worlds. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011;13:31–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

